Merge branch 'main' into dev/bbl-network-upd
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
|||
},
|
||||
"options": ["--platform=linux/amd64"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"runArgs": ["--env-file", "/tmp/devcontainer.env", "--platform=linux/amd64"],
|
||||
"runArgs": ["--platform=linux/amd64"],
|
||||
"features": {
|
||||
"ghcr.io/devcontainers/features/desktop-lite:1": {
|
||||
"password": "orca"
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,9 +23,6 @@
|
|||
"-DBBL_INTERNAL_TESTING=0",
|
||||
"-DSLIC3R_STATIC=1",
|
||||
"-DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=${workspaceFolder}/deps/build/destdir/usr/local"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"cmake.buildToolArgs": [
|
||||
"-l${containerEnv:CORES}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,10 +44,6 @@
|
|||
"otherPortsAttributes": {
|
||||
"onAutoForward": "ignore"
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
"initializeCommand": {
|
||||
"Setup Temporary Env File": "echo \"CORES=`nproc --all`\" > /tmp/devcontainer.env"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"onCreateCommand": {
|
||||
"Set postCreate executable flag": "chmod +x .devcontainer/postCreate.sh"
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
219
README.md
|
|
@ -1,135 +1,130 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<h1> <p "font-size:200px;"><img align="left" src="https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/resources/images/OrcaSlicer.ico" width="100"> Orca Slicer</p> </h1>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/actions/workflows/build_all.yml)
|
||||
<br>Orca Slicer is an open source slicer for FDM printers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Follow Us
|
||||
Stay connected with us:
|
||||
Orca Slicer is an open source Next-Gen Slicing Software for Precision 3D Prints.
|
||||
Optimize your prints with ultra-fast slicing, intelligent support generation, and seamless printer compatibility—engineered for perfection.
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://twitter.com/real_OrcaSlicer)
|
||||
## Official links and community
|
||||
|
||||
Join our Discord community here:<br>
|
||||
<a href="https://discord.gg/P4VE9UY9gJ"><img src="https://img.shields.io/static/v1?message=Discord&logo=discord&label=&color=7289DA&logoColor=white&labelColor=&style=for-the-badge" height="35" alt="discord logo"/> </a>
|
||||
|
||||
<h3>🚨🚨🚨Important Security Alert🚨🚨🚨</h3>
|
||||
#### Official Website:
|
||||
<a href="https://orcaslicer.com/" style="font-size:2em;"><strong>orcaslicer.com</strong></a>
|
||||
|
||||
The only official platforms for OrcaSlicer are **our GitHub project page**, <a href="https://orcaslicer.com/">**orcaslicer.com**</a>, the <a href="https://discord.gg/P4VE9UY9gJ">**official Discord channel**</a>, and the <a href="https://twitter.com/real_OrcaSlicer">**official Twitter/X account**</a>.
|
||||
#### Github Repository:
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/OrcaSlicer-181717?style=flat&logo=github&logoColor=white" width="200" alt="GitHub Logo"/> </a>
|
||||
|
||||
Please be aware that "**orcaslicer.net**", "**orcaslicer.co**" or "**orca-slicer.com**" are NOT an official website for OrcaSlicer and may be potentially malicious. These sites appear to use AI-generated content, lacking genuine context and seems to exist solely to profit from advertisements. Worse, it may redirect download links to harmful sources. For your safety, avoid downloading OrcaSlicer from this site as the links may be compromised.
|
||||
#### Follow us:
|
||||
<a href="https://twitter.com/real_OrcaSlicer"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/real__OrcaSlicer-000000?style=flat&logo=x&logoColor=white" width="200" alt="X Logo"/> </a>
|
||||
|
||||
If you see the above sites in your searches, report them as spam or unsafe to the search engine. This small action will assist everyone.
|
||||
#### Join our Discord community:
|
||||
<a href="https://discord.gg/P4VE9UY9gJ"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/-Discord-5865F2?style=flat&logo=discord&logoColor=fff" width="200" alt="discord logo"/> </a>
|
||||
|
||||
We deeply value our OrcaSlicer community and appreciate all the social groups that support us. However, it is crucial to address the risk posed by any group that falsely claims to be official or misleads its members. If you encounter such a group or are part of one, please assist by encouraging the group owner to add a clear disclaimer or by alerting its members.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for your vigilance and support in keeping our community safe!
|
||||
> [!CAUTION]
|
||||
> There are multiple unofficial and potentially malicious websites pretending to be related to OrcaSlicer. These sites may redirect you to dangerous downloads or contain misleading information.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If you come across any of these in search results, please report them as unsafe or spam to help keep the community secure.
|
||||
|
||||
# Main features
|
||||
- Auto-calibration for all printers
|
||||
- Sandwich (inner-outer-inner) mode - An improved version of the `External Perimeters First` mode
|
||||
- [Precise wall](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki/Precise-wall)
|
||||
- Polyholes conversion support: [SuperSlicer Wiki: Polyholes](https://github.com/supermerill/SuperSlicer/wiki/Polyholes)
|
||||
- Klipper support
|
||||
- More granular controls
|
||||
- Additional features can be found in the [change notes](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/)
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Advanced Calibration Tools](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki/Calibration)**
|
||||
Comprehensive suite: temperature towers, flow rate, retraction & more for optimal performance.
|
||||
- **[Precise Wall](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki/Precise-wall) and [Seam Control](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki/quality_settings_seam)**
|
||||
Adjust outer wall spacing and apply scarf seams to enhance print accuracy.
|
||||
- **Sandwich Mode and [SuperSlicer Polyholes](https://github.com/supermerill/SuperSlicer/wiki/Polyholes) Support**
|
||||
Use varied infill patterns and accurate hole shapes for improved clarity.
|
||||
- **Overhang and Support Optimization**
|
||||
Modify geometry for printable overhangs with precise support placement.
|
||||
- **Granular Controls and Customization**
|
||||
Fine-tune print speed, layer height, pressure, and temperature with precision.
|
||||
- **Network Printer Support**
|
||||
Seamless integration with Klipper, PrusaLink, and OctoPrint for remote control.
|
||||
- **Mouse Ear Brims & Adaptive Bed Mesh**
|
||||
Automatic brims and adaptive mesh calibration ensure consistent adhesion.
|
||||
- **User-Friendly Interface**
|
||||
Intuitive drag-and-drop design with pre-made profiles for popular printers.
|
||||
- **Open-Source & Community Driven**
|
||||
Regular updates fueled by continuous community contributions.
|
||||
- **Wide Printer Compatibility**
|
||||
Supports a broad range of printers: Bambu Lab, Prusa, Creality, Voron, and more.
|
||||
- Additional features can be found in the [change notes](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/)
|
||||
|
||||
# Wiki
|
||||
|
||||
The wiki below aims to provide a detailed explanation of the slicer settings, including how to maximize their use and how to calibrate and set up your printer.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that the wiki is a work in progress. We appreciate your patience as we continue to develop and improve it!
|
||||
|
||||
**[Access the wiki here](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki)**
|
||||
**[Access the wiki here](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki)**
|
||||
**[Contribute to the wiki](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki/How-to-wiki)**
|
||||
|
||||
# Download
|
||||
|
||||
### Stable Release
|
||||
## Stable Release
|
||||
📥 **[Download the Latest Stable Release](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/latest)**
|
||||
Visit our GitHub Releases page for the latest stable version of Orca Slicer, recommended for most users.
|
||||
|
||||
### Nightly Builds
|
||||
## Nightly Builds
|
||||
🌙 **[Download the Latest Nightly Build](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/tag/nightly-builds)**
|
||||
Explore the latest developments in Orca Slicer with our nightly builds. Feedback on these versions is highly appreciated.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# How to install
|
||||
**Windows**:
|
||||
1. Download the installer for your preferred version from the [releases page](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases).
|
||||
- *For convenience there is also a portable build available.*
|
||||
- *If you have troubles to run the build, you might need to install following runtimes:*
|
||||
- [MicrosoftEdgeWebView2RuntimeInstallerX64](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/download/v1.0.10-sf2/MicrosoftEdgeWebView2RuntimeInstallerX64.exe)
|
||||
- [Details of this runtime](https://aka.ms/webview2)
|
||||
- [Alternative Download Link Hosted by Microsoft](https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=2124703)
|
||||
- [vcredist2019_x64](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/download/v1.0.10-sf2/vcredist2019_x64.exe)
|
||||
- [Alternative Download Link Hosted by Microsoft](https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vc_redist.x64.exe)
|
||||
- This file may already be available on your computer if you've installed visual studio. Check the following location: `%VCINSTALLDIR%Redist\MSVC\v142`
|
||||
## Windows
|
||||
Download the **Windows Installer exe** for your preferred version from the [releases page](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases).
|
||||
|
||||
- *For convenience there is also a portable build available.*
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Troubleshooting</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
- *If you have troubles to run the build, you might need to install following runtimes:*
|
||||
- [MicrosoftEdgeWebView2RuntimeInstallerX64](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/download/v1.0.10-sf2/MicrosoftEdgeWebView2RuntimeInstallerX64.exe)
|
||||
- [Details of this runtime](https://aka.ms/webview2)
|
||||
- [Alternative Download Link Hosted by Microsoft](https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=2124703)
|
||||
- [vcredist2019_x64](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/releases/download/v1.0.10-sf2/vcredist2019_x64.exe)
|
||||
- [Alternative Download Link Hosted by Microsoft](https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vc_redist.x64.exe)
|
||||
- This file may already be available on your computer if you've installed visual studio. Check the following location: `%VCINSTALLDIR%Redist\MSVC\v142`
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
Windows Package Manager:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
winget install --id=SoftFever.OrcaSlicer --e
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Mac:
|
||||
1. Download the DMG for your computer: `arm64` version for Apple Silicon and `x86_64` for Intel CPU.
|
||||
2. Drag OrcaSlicer.app to Application folder.
|
||||
3. *If you want to run a build from a PR, you also need to follow the instructions below:*
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Quarantine</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
**Mac**:
|
||||
1. Download the DMG for your computer: `arm64` version for Apple Silicon and `x86_64` for Intel CPU.
|
||||
2. Drag OrcaSlicer.app to Application folder.
|
||||
3. *If you want to run a build from a PR, you also need to follow the instructions below:*
|
||||
<details quarantine>
|
||||
- Option 1 (You only need to do this once. After that the app can be opened normally.):
|
||||
- Step 1: Hold _cmd_ and right click the app, from the context menu choose **Open**.
|
||||
- Step 2: A warning window will pop up, click _Open_
|
||||
|
||||
- Option 2:
|
||||
Execute this command in terminal: `xattr -dr com.apple.quarantine /Applications/OrcaSlicer.app`
|
||||
```console
|
||||
softfever@mac:~$ xattr -dr com.apple.quarantine /Applications/OrcaSlicer.app
|
||||
- Step 2: A warning window will pop up, click _Open_
|
||||
|
||||
- Option 2:
|
||||
Execute this command in terminal:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
xattr -dr com.apple.quarantine /Applications/OrcaSlicer.app`
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Option 3:
|
||||
- Option 3:
|
||||
- Step 1: open the app, a warning window will pop up
|
||||

|
||||
- Step 2: in `System Settings` -> `Privacy & Security`, click `Open Anyway`:
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
- Step 2: in `System Settings` -> `Privacy & Security`, click `Open Anyway`:
|
||||

|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
**Linux (Ubuntu)**:
|
||||
1. If you run into trouble executing it, try this command in the terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
## Linux (Ubuntu):
|
||||
1. If you run into trouble executing it, try this command in the terminal:
|
||||
`chmod +x /path_to_appimage/OrcaSlicer_Linux.AppImage`
|
||||
|
||||
# How to compile
|
||||
- Windows 64-bit
|
||||
- Tools needed: Visual Studio 2019, Cmake, git, git-lfs, Strawberry Perl.
|
||||
- You will require cmake version 3.14 or later, which is available [on their website](https://cmake.org/download/).
|
||||
- Strawberry Perl is [available on their GitHub repository](https://github.com/StrawberryPerl/Perl-Dist-Strawberry/releases/).
|
||||
- Run `build_release.bat` in `x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019`
|
||||
- Note: Don't forget to run `git lfs pull` after cloning the repository to download tools on Windows
|
||||
|
||||
- Mac 64-bit
|
||||
- Tools needed: Xcode, Cmake, git, gettext, libtool, automake, autoconf, texinfo
|
||||
- You can install most of them by running `brew install cmake gettext libtool automake autoconf texinfo`
|
||||
- If you haven't since upgrading Xcode, start Xcode and install macOS build support.
|
||||
- run `build_release_macos.sh`
|
||||
- open `build_arm64/OrcaSlicer/OrcaSlicer.app`
|
||||
- To build and debug in Xcode:
|
||||
- run `Xcode.app`
|
||||
- open ``build_`arch`/OrcaSlicer.Xcodeproj``
|
||||
- menu bar: Product => Scheme => OrcaSlicer
|
||||
- menu bar: Product => Scheme => Edit Scheme...
|
||||
- Run => Info tab => Build Configuration: `RelWithDebInfo`
|
||||
- Run => Options tab => Document Versions: uncheck `Allow debugging when browsing versions`
|
||||
- menu bar: Product => Run
|
||||
# How to Compile
|
||||
All updated build instructions for Windows, macOS, and Linux are now available on the official [OrcaSlicer Wiki - How to build](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/wiki/How-to-build) page.
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux (All Distros)
|
||||
- Docker
|
||||
- Dependencies: Docker [Installation Instructions](https://www.docker.com/get-started/), git
|
||||
- clone this repository `git clone https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer`
|
||||
- run `cd OrcaSlicer`
|
||||
- run `./DockerBuild.sh`
|
||||
- To run OrcaSlicer:
|
||||
- run `./DockerRun.sh`
|
||||
- For most common errors, open `DockerRun.sh` and read the comments.
|
||||
- Ubuntu
|
||||
- Dependencies **Will be auto installed with the shell script**: `libmspack-dev libgstreamerd-3-dev libsecret-1-dev libwebkit2gtk-4.0-dev libosmesa6-dev libssl-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev eglexternalplatform-dev libudev-dev libdbus-1-dev extra-cmake-modules libgtk2.0-dev libglew-dev libudev-dev libdbus-1-dev cmake git texinfo`
|
||||
- run 'sudo ./BuildLinux.sh -u'
|
||||
- run './BuildLinux.sh -dsi'
|
||||
Please refer to the wiki to ensure you're following the latest and most accurate steps for your platform.
|
||||
|
||||
# Note:
|
||||
# Klipper Note:
|
||||
If you're running Klipper, it's recommended to add the following configuration to your `printer.cfg` file.
|
||||
```
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
# Enable object exclusion
|
||||
[exclude_object]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -139,53 +134,49 @@ resolution: 0.1
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Supports
|
||||
**Orca Slicer** is an open-source project and I'm deeply grateful to all my sponsors and backers.
|
||||
Their generous support enables me to purchase filaments and other essential 3D printing materials for the project.
|
||||
**Orca Slicer** is an open-source project and I'm deeply grateful to all my sponsors and backers.
|
||||
Their generous support enables me to purchase filaments and other essential 3D printing materials for the project.
|
||||
Thank you! :)
|
||||
|
||||
### Sponsors:
|
||||
## Sponsors:
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<a href="https://qidi3d.com/">
|
||||
<img src="SoftFever_doc\sponsor_logos\QIDI.png" alt="QIDI" width="96" height="">
|
||||
<a href="https://qidi3d.com/" style="display:inline-block; border-radius:8px; background:#fff;">
|
||||
<img src="SoftFever_doc\sponsor_logos\QIDI.png" alt="QIDI" width="100" height="100">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<a href="https://bigtree-tech.com/">
|
||||
<img src="SoftFever_doc\sponsor_logos\BigTreeTech.png" alt="BIGTREE TECH" width="96" height="">
|
||||
<a href="https://bigtree-tech.com/" style="display:inline-block; border-radius:8px; background:#222;">
|
||||
<img src="SoftFever_doc\sponsor_logos\BigTreeTech.png" alt="BIGTREE TECH" width="100" height="100">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Backers:
|
||||
**Ko-fi supporters**: [Backers list](https://github.com/user-attachments/files/16147016/Supporters_638561417699952499.csv)
|
||||
|
||||
## Support me
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/sponsors/SoftFever"><img src="https://img.shields.io/static/v1?label=Sponsor&message=%E2%9D%A4&logo=GitHub&color=%23fe8e86" width="130"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://ko-fi.com/G2G5IP3CP"><img src="https://ko-fi.com/img/githubbutton_sm.svg" width="200"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://paypal.me/softfever3d)
|
||||
## Backers:
|
||||
**Ko-fi supporters** ☕: [Backers list](https://github.com/user-attachments/files/16147016/Supporters_638561417699952499.csv)
|
||||
|
||||
## Support me
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/sponsors/SoftFever"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/GitHub%20Sponsors-30363D?style=flat&logo=GitHub-Sponsors&logoColor=EA4AAA" height="50"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://ko-fi.com/G2G5IP3CP"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Support_me_on_Ko--fi-FF5E5B?style=flat&logo=ko-fi&logoColor=white" height="50"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://paypal.me/softfever3d"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/PayPal-003087?style=flat&logo=paypal&logoColor=fff" height="50"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Some background
|
||||
OrcaSlicer was originally forked from Bambu Studio, it was previously known as BambuStudio-SoftFever.
|
||||
|
||||
[Bambu Studio](https://github.com/bambulab/BambuStudio) is forked from [PrusaSlicer](https://github.com/prusa3d/PrusaSlicer) by Prusa Research, which is from [Slic3r](https://github.com/Slic3r/Slic3r) by Alessandro Ranellucci and the RepRap community.
|
||||
Orca Slicer incorporates a lot of features from [SuperSlicer](https://github.com/supermerill/SuperSlicer) by @supermerill
|
||||
Orca Slicer's logo is designed by community member Justin Levine(@freejstnalxndr)
|
||||
|
||||
Orca Slicer's logo is designed by community member Justin Levine(@freejstnalxndr).
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||
Orca Slicer is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. Orca Slicer is based on Bambu Studio by BambuLab.
|
||||
**Orca Slicer** is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. Orca Slicer is based on Bambu Studio by BambuLab.
|
||||
|
||||
Bambu Studio is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. Bambu Studio is based on PrusaSlicer by PrusaResearch.
|
||||
**Bambu Studio** is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. Bambu Studio is based on PrusaSlicer by PrusaResearch.
|
||||
|
||||
PrusaSlicer is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. PrusaSlicer is owned by Prusa Research. PrusaSlicer is originally based on Slic3r by Alessandro Ranellucci.
|
||||
**PrusaSlicer** is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. PrusaSlicer is owned by Prusa Research. PrusaSlicer is originally based on Slic3r by Alessandro Ranellucci.
|
||||
|
||||
Slic3r is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. Slic3r was created by Alessandro Ranellucci with the help of many other contributors.
|
||||
**Slic3r** is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3. Slic3r was created by Alessandro Ranellucci with the help of many other contributors.
|
||||
|
||||
The GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 ensures that if you use any part of this software in any way (even behind a web server), your software must be released under the same license.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -37,14 +37,6 @@
|
|||
<array>
|
||||
<string>orcaslicer</string>
|
||||
</array>
|
||||
</dict>
|
||||
<dict>
|
||||
<key>CFBundleURLName</key>
|
||||
<string>BambuStudio Downloads</string>
|
||||
<key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key>
|
||||
<array>
|
||||
<string>bambustudioopen</string>
|
||||
</array>
|
||||
</dict>
|
||||
</array>
|
||||
<key>CFBundleDocumentTypes</key>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,10 +1,14 @@
|
|||
# Auxiliary Fan
|
||||
|
||||
OrcaSlicer use `M106 P2` command to control auxiliary cooling fan.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Klipper, you can define a `M106` macro to control the both normal part cooling fan and auxiliary fan and exhaust fan.
|
||||
Below is a reference configuration for Klipper.
|
||||
*Note: Don't forget to change the pin name to the actual pin name you are using in the configuration*
|
||||
If you are using Klipper, you can define a `M106` macro to control the both normal part cooling fan and auxiliary fan and exhaust fan.
|
||||
Below is a reference configuration for Klipper.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Don't forget to change the pin name to the actual pin name you are using in the configuration
|
||||
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
# instead of using [fan], we define the default part cooling fan with [fan_generic] here
|
||||
# this is the default part cooling fan
|
||||
[fan_generic fan0]
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,5 +35,4 @@ gcode:
|
|||
{% set fan = 'fan' + (params.P|int if params.P is defined else 0)|string %}
|
||||
{% set speed = (params.S|float / 255 if params.S is defined else 1.0) %}
|
||||
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={fan} SPEED={speed}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,343 +0,0 @@
|
|||
- [Flow rate](#flow-rate)
|
||||
- [Pressure Advance](#pressure-advance)
|
||||
- [Line method](#line-method)
|
||||
- [Pattern method](#pattern-method)
|
||||
- [Tower method](#tower-method)
|
||||
- [Temp tower](#temp-tower)
|
||||
- [Retraction test](#retraction-test)
|
||||
- [Orca Tolerance Test](#orca-tolerance-test)
|
||||
- [Advanced Calibration](#advanced-calibration)
|
||||
- [Max Volumetric speed](#max-volumetric-speed)
|
||||
- [Input Shaping](#input-shaping)
|
||||
- [Klipper](#klipper)
|
||||
- [Resonance Compensation](#resonance-compensation)
|
||||
- [Marlin](#marlin)
|
||||
- [ZV Input Shaping](#zv-input-shaping)
|
||||
- [Fixed-Time Motion](#fixed-time-motion)
|
||||
- [Junction Deviation](#junction-deviation)
|
||||
- [VFA](#vfa)
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> After completing the calibration process, remember to create a new project in order to exit the calibration mode.
|
||||
|
||||
# Flow rate
|
||||
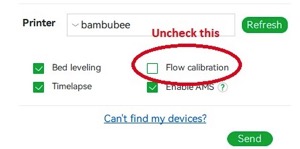
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> For Bambulab X1/X1C users, make sure you do not select the 'Flow calibration' option.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> PASS 1 and PASS 2 follow the older flow ratio formula `FlowRatio_old*(100 + modifier)/100`. YOLO (Recommended) and YOLO (perfectist version) use a new system that is very simple `FlowRatio_old±modifier`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Calibrating the flow rate involves a two-step process.
|
||||
Steps
|
||||
1. Select the printer, filament, and process you would like to use for the test.
|
||||
2. Select `Pass 1` in the `Calibration` menu
|
||||
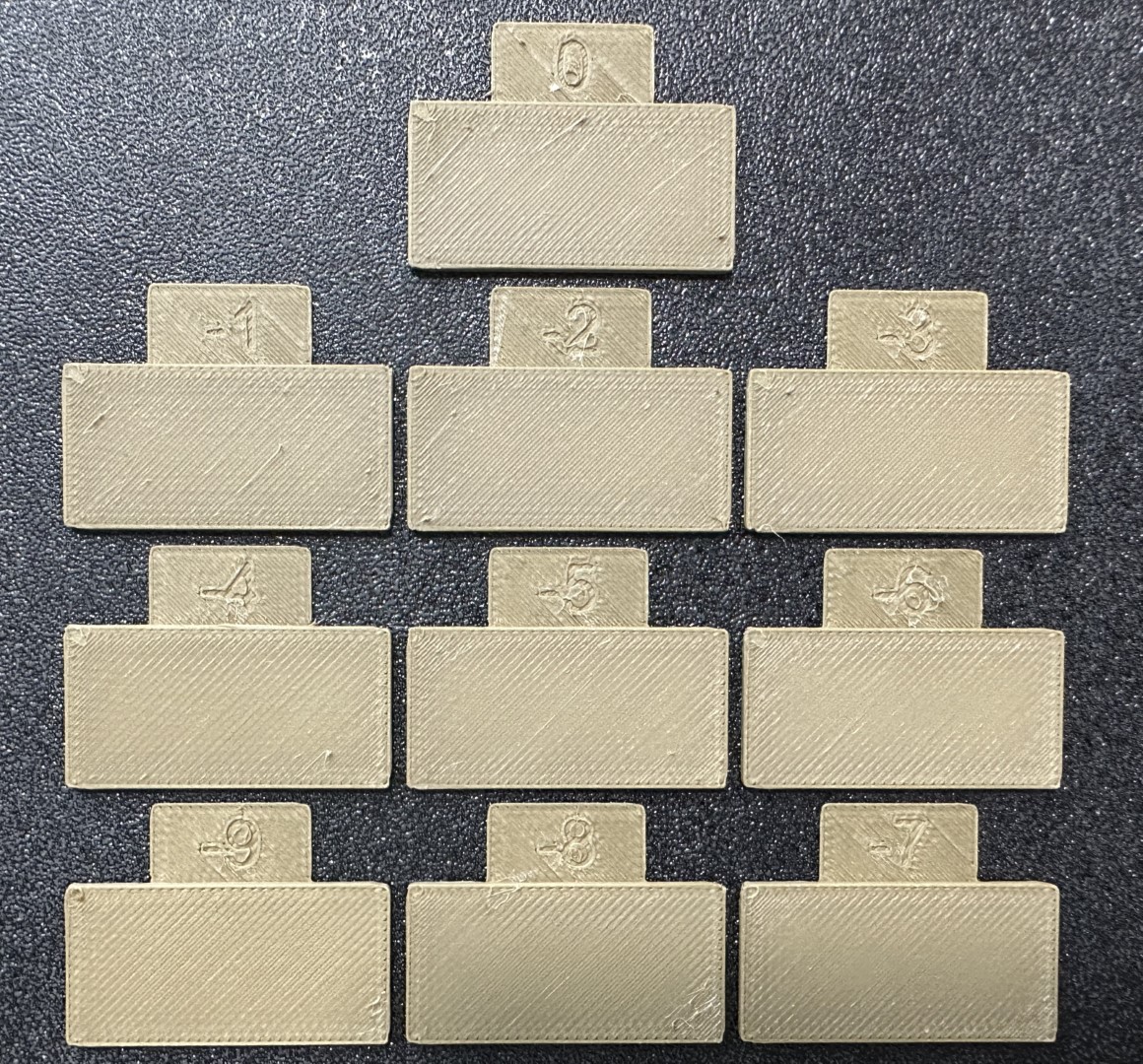
3. A new project consisting of nine blocks will be created, each with a different flow rate modifier. Slice and print the project.
|
||||
4. Examine the blocks and determine which one has the smoothest top surface.
|
||||

|
||||
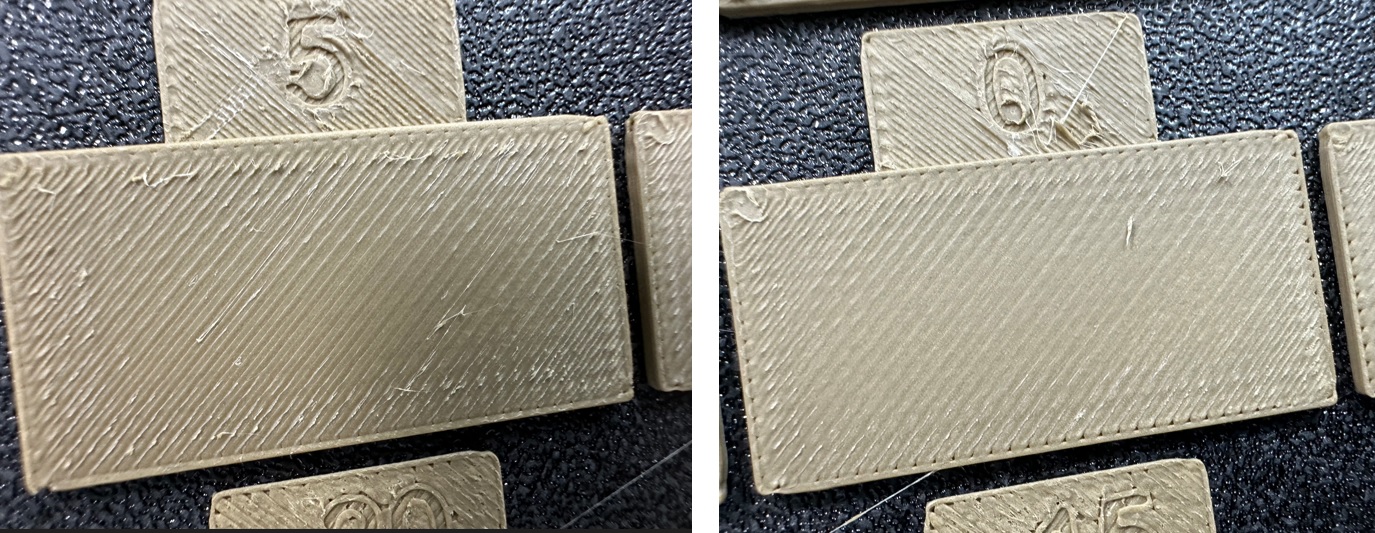

|
||||
|
||||
5. Update the flow ratio in the filament settings using the following equation: `FlowRatio_old*(100 + modifier)/100`. If your previous flow ratio was `0.98` and you selected the block with a flow rate modifier of `+5`, the new value should be calculated as follows: `0.98x(100+5)/100 = 1.029`.** Remember** to save the filament profile.
|
||||
6. Perform the `Pass 2` calibration. This process is similar to `Pass 1`, but a new project with ten blocks will be generated. The flow rate modifiers for this project will range from `-9 to 0`.
|
||||
7. Repeat steps 4. and 5. In this case, if your previous flow ratio was 1.029 and you selected the block with a flow rate modifier of -6, the new value should be calculated as follows: `1.029x(100-6)/100 = 0.96726`. **Remember** to save the filament profile.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
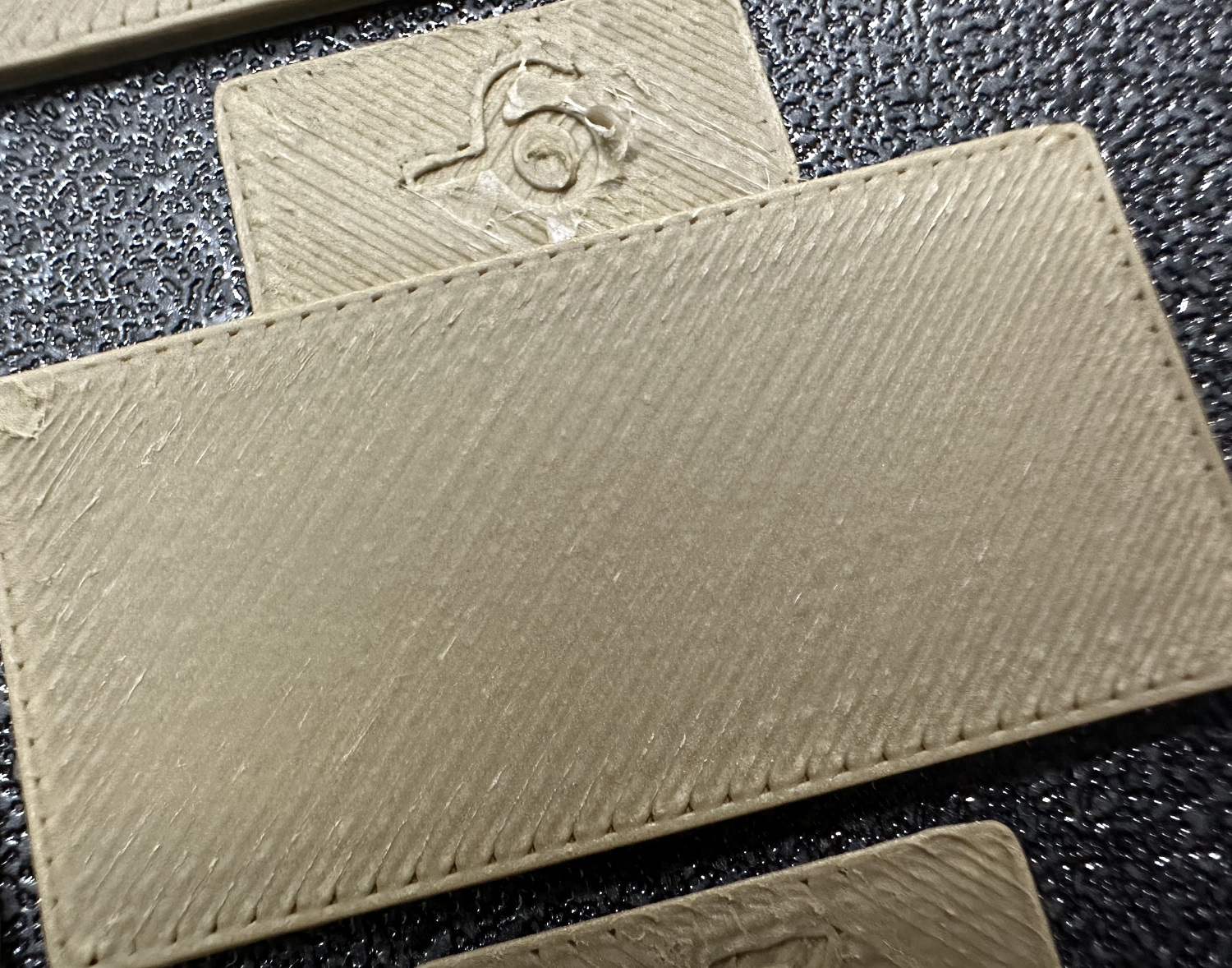

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Pressure Advance
|
||||
|
||||
Orca Slicer includes three approaches for calibrating the pressure advance value. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. It is important to note that each method has two versions: one for a direct drive extruder and one for a Bowden extruder. Make sure to select the appropriate version for your test.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> For Marlin: Linear advance must be enabled in firmware (M900). **Not all printers have it enabled by default.**
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> For Bambulab X1/X1C users, make sure you do not select the 'Flow calibration' option when printings.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
|
||||
### Line method
|
||||
|
||||
The line method is quick and straightforward to test. However, its accuracy highly depends on your first layer quality. It is suggested to turn on the bed mesh leveling for this test.
|
||||
Steps:
|
||||
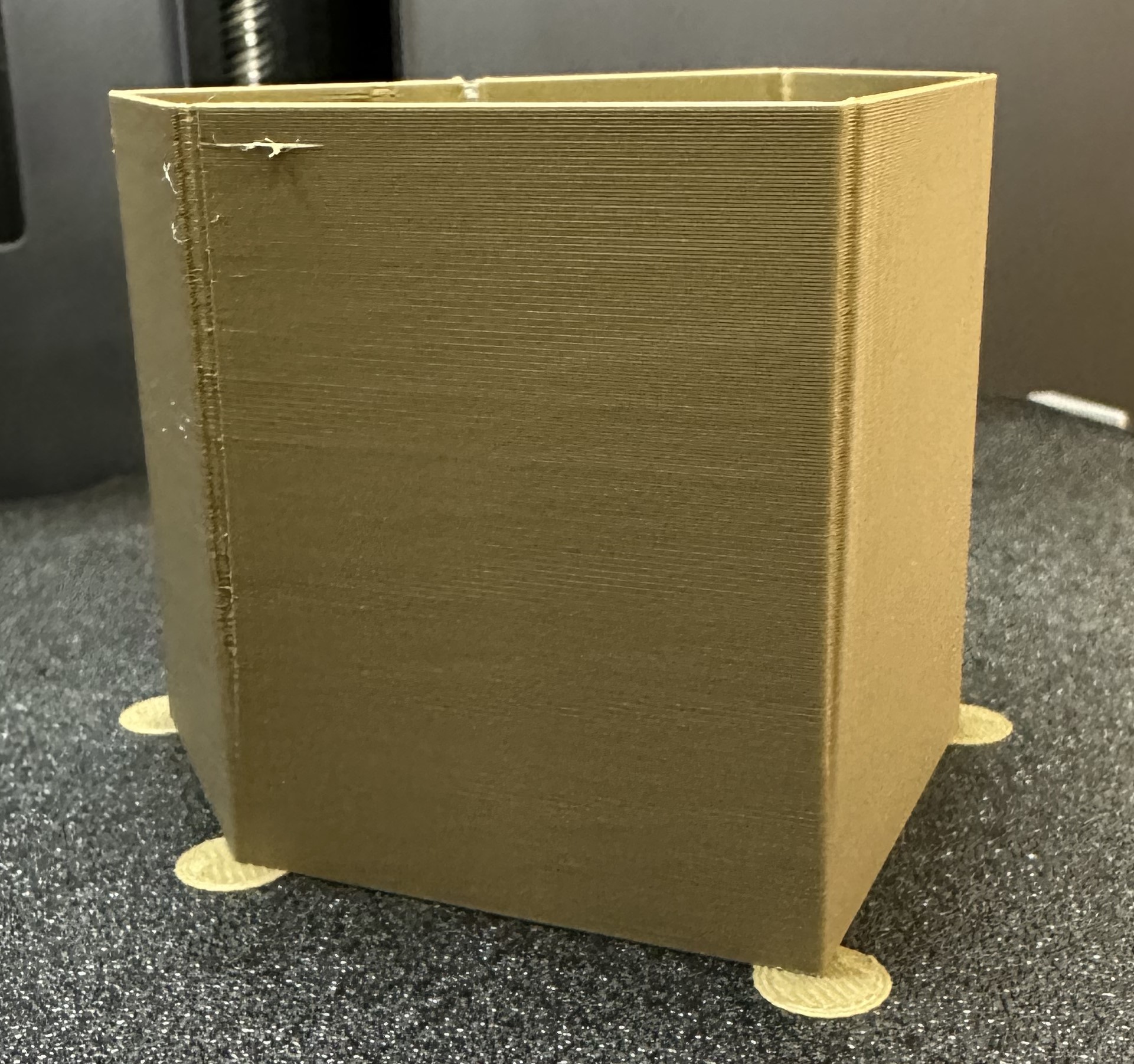
1. Select the printer, filament, and process you would like to use for the test.
|
||||
2. Print the project and check the result. You can select the value of the most even line and update your PA value in the filament settings.
|
||||
3. In this test, a PA value of `0.016` appears to be optimal.
|
||||
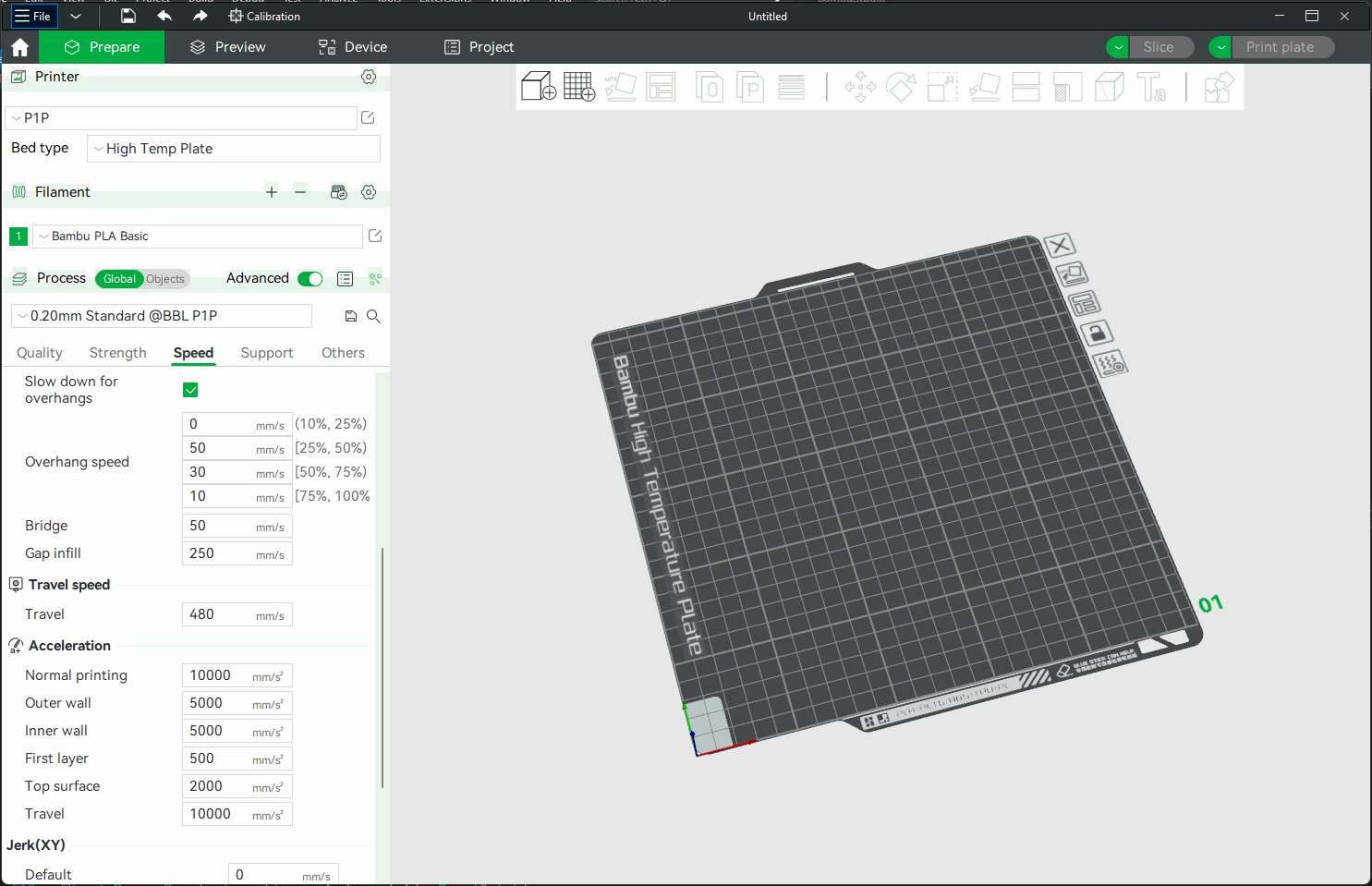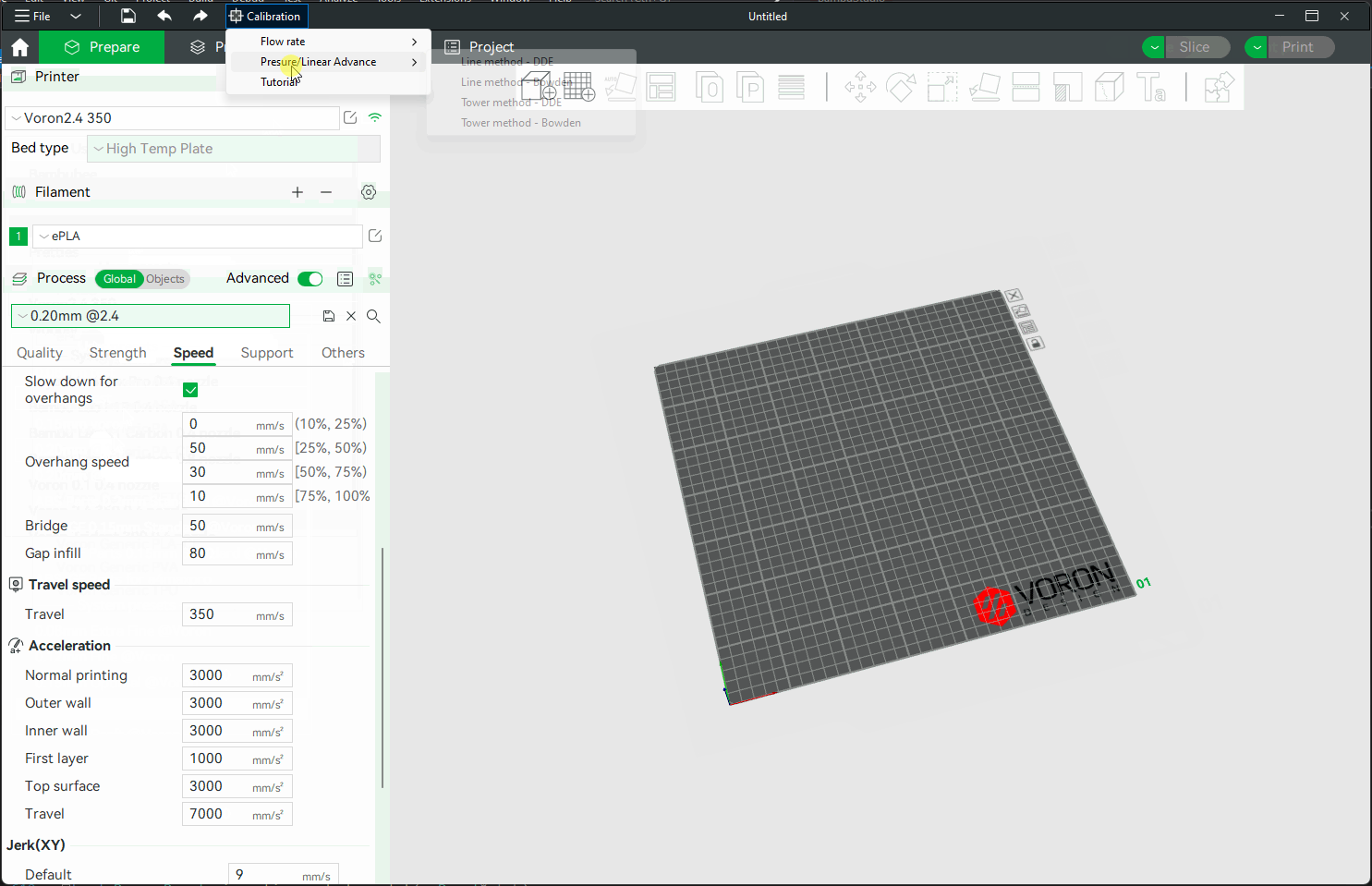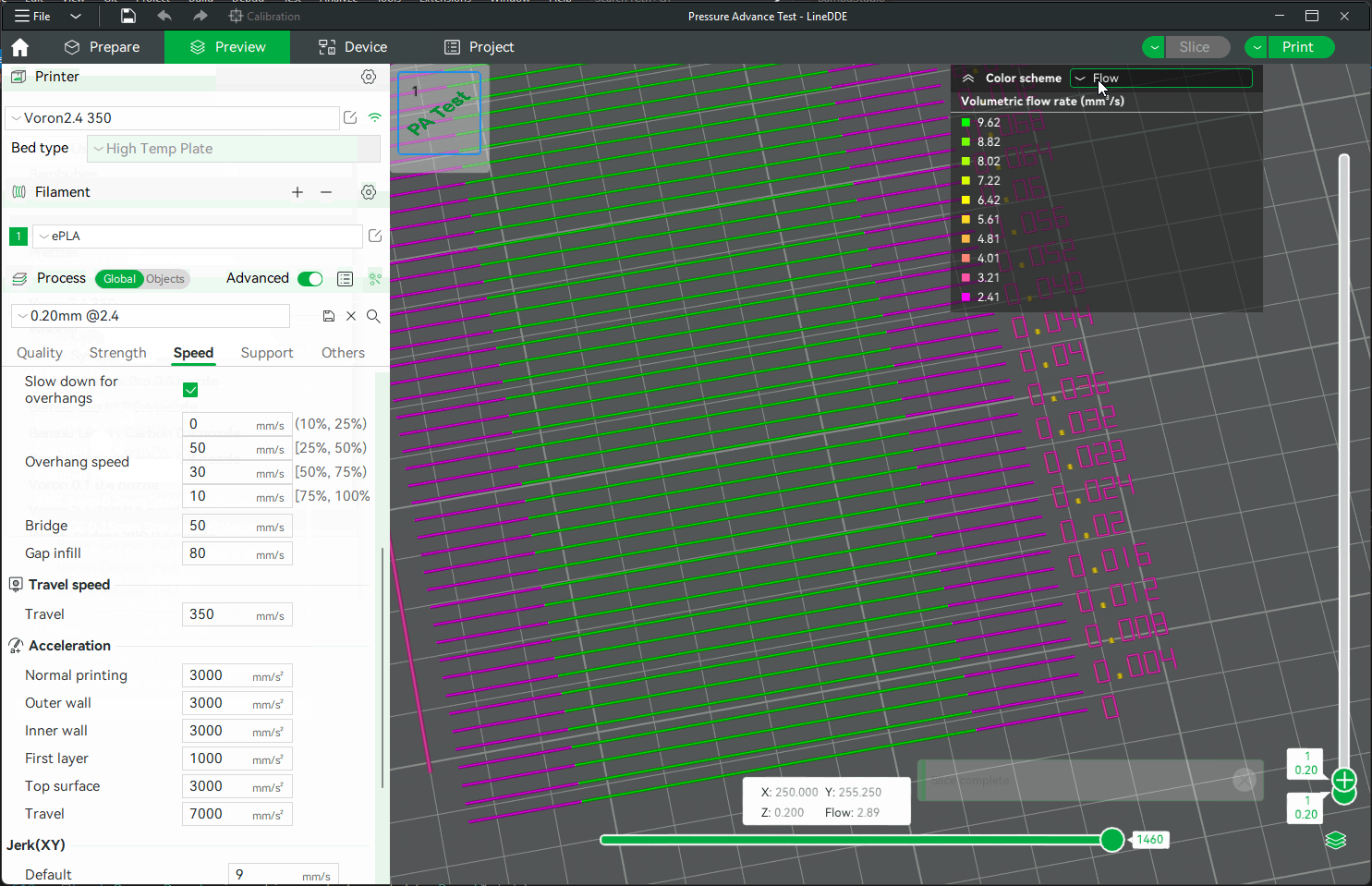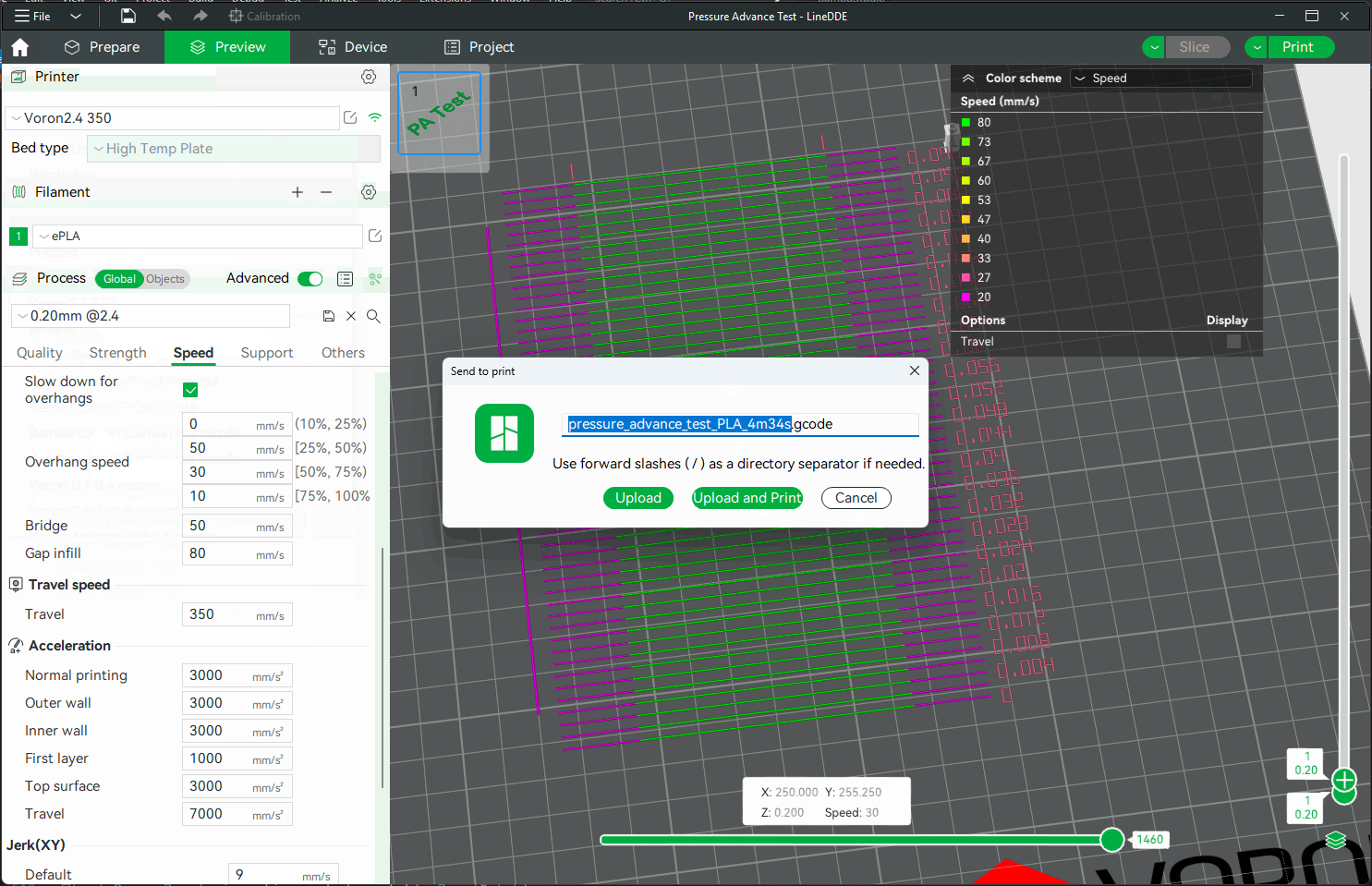
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1003" alt="Screenshot 2022-12-31 at 12 11 10 PM" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/103989404/210124449-dd828da8-a7e4-46b8-9fa2-8bed5605d9f6.png">
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Pattern method
|
||||
|
||||
The pattern method is adapted from [Andrew Ellis' pattern method generator](https://ellis3dp.com/Pressure_Linear_Advance_Tool/), which was itself derived from the [Marlin pattern method](https://marlinfw.org/tools/lin_advance/k-factor.html) developed by [Sineos](https://github.com/Sineos/k-factorjs).
|
||||
|
||||
[Instructions for using and reading the pattern method](https://ellis3dp.com/Print-Tuning-Guide/articles/pressure_linear_advance/pattern_method.html) are provided in [Ellis' Print Tuning Guide](https://ellis3dp.com/Print-Tuning-Guide/), with only a few Orca Slicer differences to note.
|
||||
|
||||
Test configuration window allow user to generate one or more tests in a single projects. Multiple tests will be placed on each plate with extra plates added if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Single test \
|
||||

|
||||
2. Batch mode testing (multiple tests on a sinle plate) \
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once test generated, one or more small rectangular prisms could be found on the plate, one for each test case. This object serves a few purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The test pattern itself is added in as custom G-Code at each layer, same as you could do by hand actually. The rectangular prism gives us the layers in which to insert that G-Code. This also means that **you'll see the full test pattern when you move to the Preview pane**:
|
||||

|
||||
2. The prism acts as a handle, enabling you to move the test pattern wherever you'd like on the plate by moving the prism
|
||||
3. Each test object is pre-configured with target parameters which are reflected in the objects name. However, test parameters may be adjusted for each prism individually by referring to the object list pane:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, Ellis' generator provided the ability to adjust specific printer, filament, and print profile settings. You can make these same changes in Orca Slicer by adjusting the settings in the Prepare pane as you would with any other print. When you initiate the calibration test, Ellis' default settings are applied. A few things to note about these settings:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ellis specified line widths as a percent of filament diameter. The Orca pattern method does the same to provide its suggested defaults, making use of Ellis' percentages in combination with your specified nozzle diameter
|
||||
2. In terms of line width, the pattern only makes use of the `Default` and `First layer` widths
|
||||
3. In terms of speed, the pattern only uses the `First layer speed -> First layer` and `Other layers speed -> Outer wall` speeds
|
||||
4. The infill pattern beneath the numbers cannot be changed becuase it's not actually an infill pattern pulled from the settings. All of the pattern G-Code is custom written, so that "infill" is, effectively, hand-drawn and so not processed through the usual channels that would enable Orca to recognize it as infill
|
||||
|
||||
### Tower method
|
||||
|
||||
The tower method may take a bit more time to complete, but it does not rely on the quality of the first layer.
|
||||
The PA value for this test will be increased by 0.002 for every 1 mm increase in height. (**NOTE** 0.02 for Bowden)
|
||||
Steps:
|
||||
1. Select the printer, filament, and process you would like to use for the test.
|
||||
2. Examine each corner of the print and mark the height that yields the best overall result.
|
||||
3. I selected a height of 8 mm for this case, so the pressure advance value should be calculated as `PressureAdvanceStart+(PressureAdvanceStep x measured)` example: `0+(0.002 x 8) = 0.016`.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
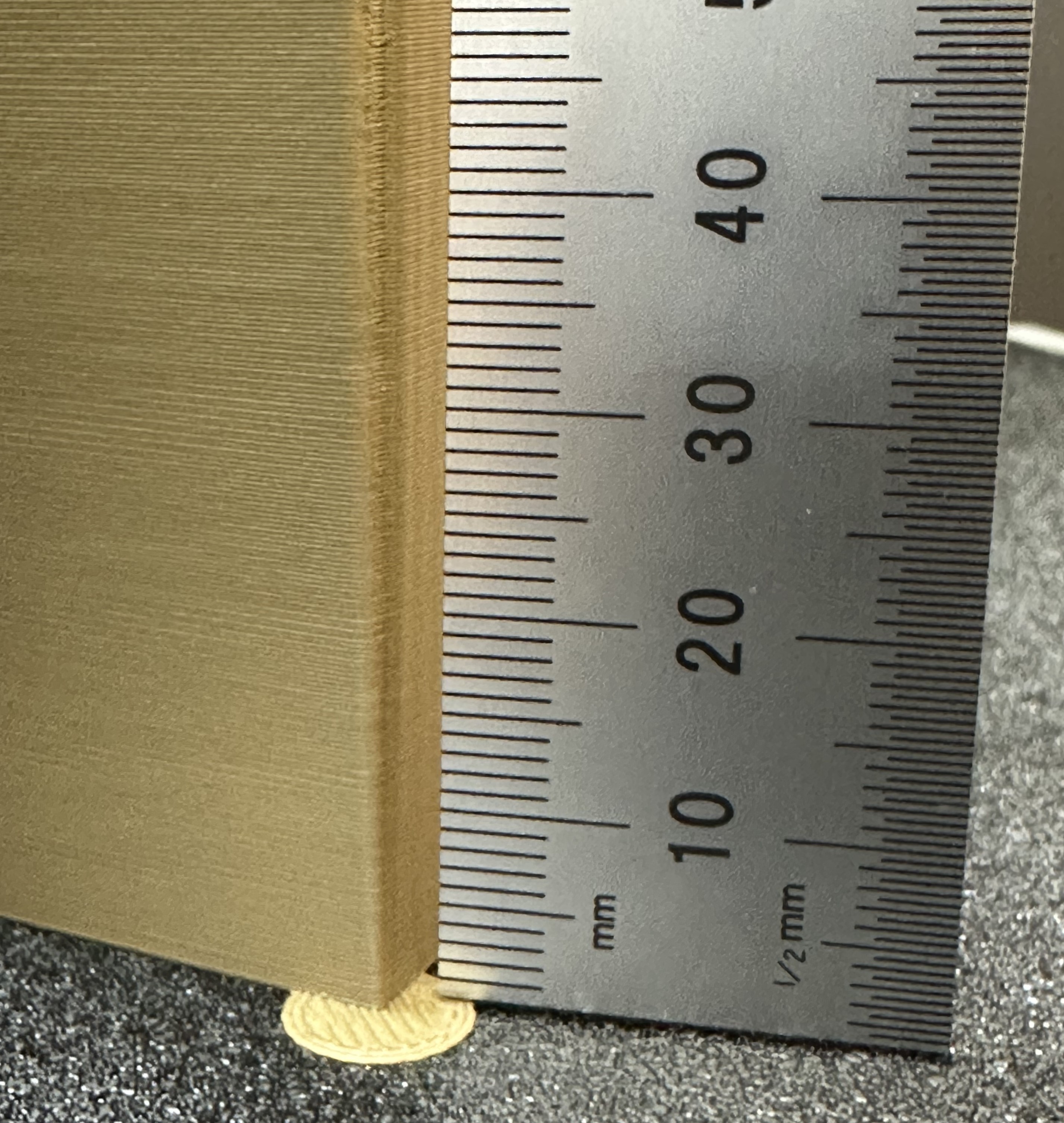
|
||||
|
||||
# Temp tower
|
||||

|
||||
Temp tower is a straightforward test. The temp tower is a vertical tower with multiple blocks, each printed at a different temperature. Once the print is complete, we can examine each block of the tower and determine the optimal temperature for the filament. The optimal temperature is the one that produces the highest quality print with the least amount of issues, such as stringing, layer adhesion, warping (overhang), and bridging.
|
||||
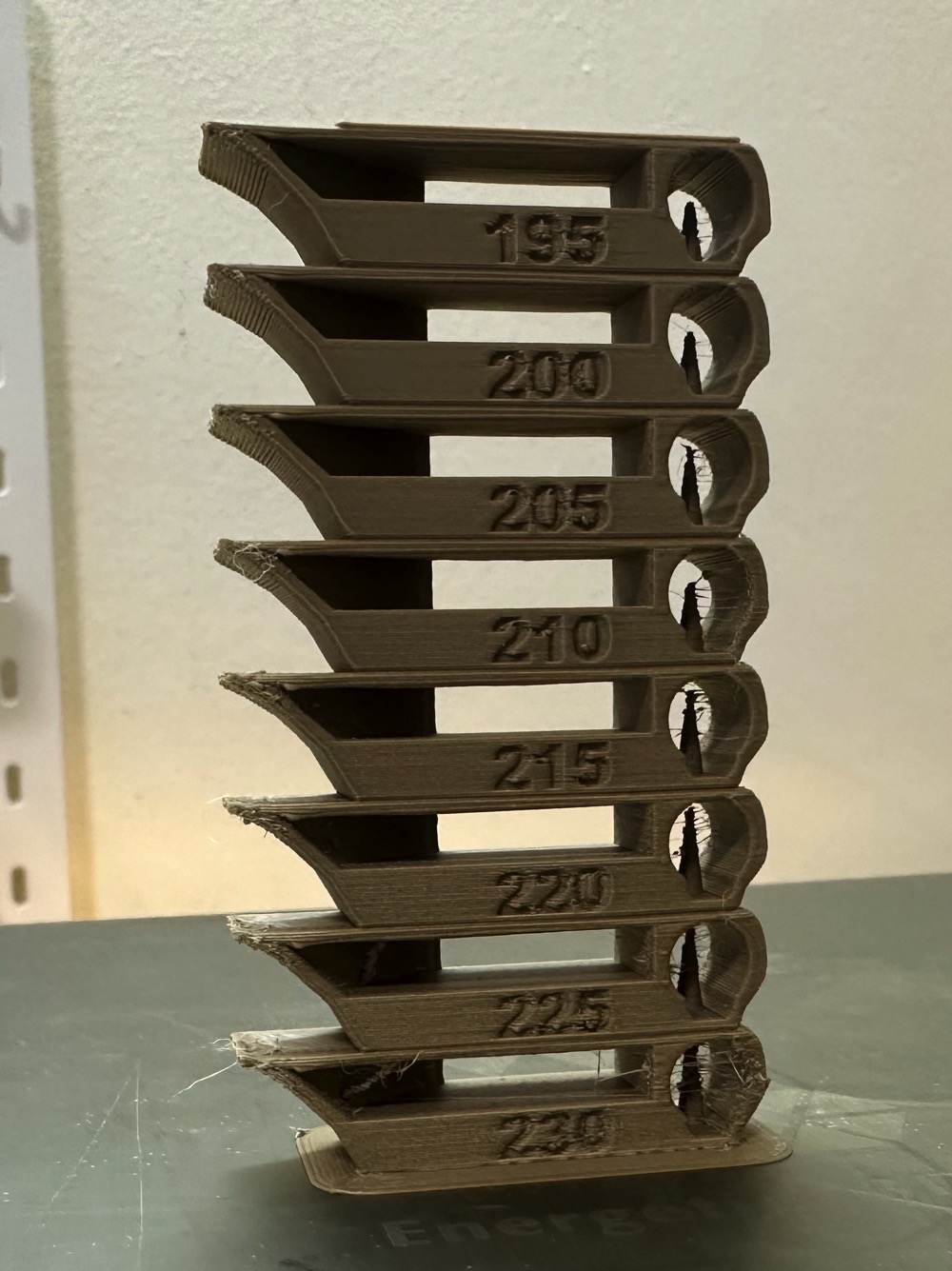

|
||||
|
||||
# Retraction test
|
||||

|
||||
This test generates a retraction tower automatically. The retraction tower is a vertical structure with multiple notches, each printed at a different retraction length. After the print is complete, we can examine each section of the tower to determine the optimal retraction length for the filament. The optimal retraction length is the shortest one that produces the cleanest tower.
|
||||

|
||||
In the dialog, you can select the start and end retraction length, as well as the retraction length increment step. The default values are 0mm for the start retraction length, 2mm for the end retraction length, and 0.1mm for the step. These values are suitable for most direct drive extruders. However, for Bowden extruders, you may want to increase the start and end retraction lengths to 1mm and 6mm, respectively, and set the step to 0.2mm.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: When testing filaments such as PLA or ABS that have minimal oozing, the retraction settings can be highly effective. You may find that the retraction tower appears clean right from the start. In such situations, setting the retraction length to 0.2mm - 0.4mm using Orca Slicer should suffice.
|
||||
On the other hand, if there is still a lot of stringing at the top of the tower, it is recommended to dry your filament and ensure that your nozzle is properly installed without any leaks.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Orca Tolerance Test
|
||||
This tolerance test is specifically designed to assess the dimensional accuracy of your printer and filament. The model comprises a base and a hexagon tester. The base contains six hexagon hole, each with a different tolerance: 0.0mm, 0.05mm, 0.1mm, 0.2mm, 0.3mm, and 0.4mm. The dimensions of the hexagon tester are illustrated in the image.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can assess the tolerance using either an M6 Allen key or the printed hexagon tester.
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Advanced Calibration
|
||||
|
||||
## Max Volumetric speed
|
||||
This is a test designed to calibrate the maximum volumetric speed of the specific filament. The generic or 3rd party filament types may not have the correct volumetric flow rate set in the filament. This test will help you to find the maximum volumetric speed of the filament.
|
||||
|
||||
You will be promted to enter the settings for the test: start volumetric speed, end volumentric speed, and step. It is recommended to use the default values (5mm³/s start, 20mm³/s end, with a step of 0.5), unless you already have an idea of the lower or upper limit for your filament. Select "OK", slice the plate, and send it to the printer.
|
||||
|
||||
Once printed, take note of where the layers begin to fail and where the quality begins to suffer. Pay attention to changes from matte to shiny as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Using calipers or a ruler, measure the height of the print at that point. Use the following calculation to determine the correct max flow value: `start + (height-measured * step)` . For example in the photo below, and using the default setting values, the print quality began to suffer at 19mm measured, so the calculation would be: `5 + (19 * 0.5)` , or `13mm³/s` using the default values. Enter your number into the "Max volumetric speed" value in the filament settings.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also return to OrcaSlicer in the "Preview" tab, make sure the color scheme "flow" is selected. Scroll down to the layer height that you measured, and click on the toolhead slider. This will indicate the max flow level for your filmanet.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> You may also choose to conservatively reduce the flow by 5-10% to ensure print quality.
|
||||
|
||||
## Input Shaping
|
||||
|
||||
During high-speed movements, vibrations can cause a phenomenon called "ringing," where periodic ripples appear on the print surface. Input Shaping provides an effective solution by counteracting these vibrations, improving print quality and reducing wear on components without needing to significantly lower print speeds.
|
||||
|
||||
### Klipper
|
||||
|
||||
### Resonance Compensation
|
||||
|
||||
The Klipper Resonance Compensation is a set of Input Shaping modes that can be used to reduce ringing and improve print quality.
|
||||
Ussualy the recommended values modes are ``MZV`` or ``EI`` for Delta printers.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Pre-requisites:
|
||||
1. In OrcaSlicer, set:
|
||||
1. Acceleration high enough to trigger ringing (e.g., 2000 mm/s²).
|
||||
2. Speed high enough to trigger ringing (e.g., 200 mm/s).
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> These settings depend on your printer's motion ability and the filament's max volumetric speed. If you can't reach speeds that cause ringing, try increasing the filament's max volumetric speed (avoid materials below 10 mm³/s).
|
||||
3. Jerk [Klipper Square Corner Velocity](https://www.klipper3d.org/Kinematics.html?h=square+corner+velocity#look-ahead) to 5 or a high value (e.g., 20).
|
||||
2. In printer settigs:
|
||||
1. Set the Shaper Type to ``MZV`` or ``EI``.
|
||||
```
|
||||
SET_INPUT_SHAPER SHAPER_TYPE=MZV
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Disable [Minimun Cruise Ratio](https://www.klipper3d.org/Kinematics.html#minimum-cruise-ratio) with:
|
||||
```
|
||||
SET_VELOCITY_LIMIT MINIMUM_CRUISE_RATIO=0
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Use an opaque, high-gloss filament to make the ringing more visible.
|
||||
2. Print the Input Shaping Frequency test with a range of frequencies.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Measure the X and Y heights and read the frequency set at that point in Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. If not a clear result, you can measure a X and Y min and max acceptable heights and repeat the test with that min and max value.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: There is a chance you will need to set higher than 60Hz frequencies. Some printers with very rigid frames and excellent mechanics may exhibit frequencies exceeding 100Hz.
|
||||
3. Print the Damping test setting your X and Y frequency to the value you found in the previous step.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Measure the X and Y heights and read the damping set at that point in Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Not all Resonance Compensation modes support damping
|
||||
4. Restore your 3D Printer settings to avoid keep using high acceleration and jerk values.
|
||||
5. Save the settings
|
||||
1. You need to go to the printer settings and set the X and Y frequency and damp to the value you found in the previous step.
|
||||
|
||||
### Marlin
|
||||
|
||||
#### ZV Input Shaping
|
||||
|
||||
ZV Input Shaping introduces an anti-vibration signal into the stepper motion for the X and Y axes. It works by splitting the step count into two halves: the first at half the frequency and the second as an "echo," delayed by half the ringing interval. This simple approach effectively reduces vibrations, improving print quality and allowing for higher speeds.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Pre-requisites:
|
||||
1. In OrcaSlicer, set:
|
||||
1. Acceleration high enough to trigger ringing (e.g., 2000 mm/s²).
|
||||
2. Speed high enough to trigger ringing (e.g., 200 mm/s).
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> These settings depend on your printer's motion ability and the filament's max volumetric speed. If you can't reach speeds that cause ringing, try increasing the filament's max volumetric speed (avoid materials below 10 mm³/s).
|
||||
4. Jerk
|
||||
1. If using [Classic Jerk](https://marlinfw.org/docs/configuration/configuration.html#jerk-) use a high value (e.g., 20).
|
||||
2. If using [Junction Deviation](https://marlinfw.org/docs/features/junction_deviation.html) (new Marlin default mode) this test will use 0.25 (high enough to most printers).
|
||||
2. Use an opaque, high-gloss filament to make the ringing more visible.
|
||||
2. Print the Input Shaping Frequency test with a range of frequencies.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Measure the X and Y heights and read the frequency set at that point in Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. If not a clear result, you can measure a X and Y min and max acceptable heights and repeat the test with that min and max value.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: There is a chance you will need to set higher than 60Hz frequencies. Some printers with very rigid frames and excellent mechanics may exhibit frequencies exceeding 100Hz.
|
||||
3. Print the Damping test setting your X and Y frequency to the value you found in the previous step.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Measure the X and Y heights and read the damping set at that point in Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4. Restore your 3D Printer settings to avoid keep using high acceleration and jerk values.
|
||||
1. Reboot your printer.
|
||||
2. Use the following G-code to restore your printer settings:
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M501
|
||||
```
|
||||
5. Save the settings
|
||||
1. You need to go to the printer settings and set the X and Y frequency and damp to the value you found in the previous step.
|
||||
2. Use the following G-code to set the frequency:
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M593 X F#Xfrequency D#XDamping
|
||||
M593 Y F#Yfrequency D#YDamping
|
||||
M500
|
||||
```
|
||||
Example
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M593 X F37.25 D0.16
|
||||
M593 Y F37.5 D0.06
|
||||
M500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fixed-Time Motion
|
||||
|
||||
TODO This calibration test is currently under development. See the [Marlin documentation](https://marlinfw.org/docs/gcode/M493.html) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Junction Deviation
|
||||
|
||||
Junction Deviation is the default method for controlling cornering speed in MarlinFW printers.
|
||||
Higher values result in more aggressive cornering speeds, while lower values produce smoother, more controlled cornering.
|
||||
The default value in Marlin is typically set to 0.08mm, which may be too high for some printers, potentially causing ringing. Consider lowering this value to reduce ringing, but avoid setting it too low, as this could lead to excessively slow cornering speeds.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Pre-requisites:
|
||||
1. Check if your printer has Junction Deviation enabled. You can do this by sending the command `M503` to your printer and looking for the line `Junction deviation: 0.25`.
|
||||
2. In OrcaSlicer, set:
|
||||
1. Acceleration high enough to trigger ringing (e.g., 2000 mm/s²).
|
||||
2. Speed high enough to trigger ringing (e.g., 100 mm/s).
|
||||
3. Use an opaque, high-gloss filament to make the ringing more visible.
|
||||
2. You need to print the Junction Deviation test.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Measure the X and Y heights and read the frequency set at that point in Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. It’s very likely that you’ll need to set values lower than 0.08 mm, as shown in the previous example. To determine a more accurate maximum JD value, you can print a new calibration tower with a maximum value set at the point where the corners start losing sharpness.
|
||||
3.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4. Measure the X and Y heights and read the frequency set at that point in Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
3. Save the settings
|
||||
1. Set your Maximun Junction Deviation value in [Printer settings/Motion ability/Jerk limitation].
|
||||
2. Use the following G-code to set the mm:
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M205 J#JunctionDeviationValue
|
||||
M500
|
||||
```
|
||||
Example
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M205 J0.012
|
||||
M500
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Recompile your MarlinFW
|
||||
1. In Configuration.h uncomment and set:
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#define JUNCTION_DEVIATION_MM 0.012 // (mm) Distance from real junction edge
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Check Classic Jerk is disabled (commented).
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
//#define CLASSIC_JERK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## VFA
|
||||
|
||||
Vertical Fine Artifacts (VFA) are small artifacts that can occur on the surface of a 3D print, particularly in areas where there are sharp corners or changes in direction. These artifacts can be caused by a variety of factors, including mechanical vibrations, resonance, and other factors that can affect the quality of the print.
|
||||
Because of the nature of these artifacts the methods to reduce them can be mechanical such as changing motors, belts and pulleys or with advanced calibrations such as Jerk/[Juction Deviation](#junction-deviation) corrections or [Input Shaping](#input-shaping).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
*Credits:*
|
||||
- *The Flowrate test and retraction test is inspired by [SuperSlicer](https://github.com/supermerill/SuperSlicer).*
|
||||
- *The PA Line method is inspired by [K-factor Calibration Pattern](https://marlinfw.org/tools/lin_advance/k-factor.html).*
|
||||
- *The PA Tower method is inspired by [Klipper](https://www.klipper3d.org/Pressure_Advance.html).*
|
||||
- *The temp tower model is remixed from [Smart compact temperature calibration tower](https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2729076).*
|
||||
- *The max flowrate test was inspired by Stefan (CNC Kitchen), and the model used in the test is a remix of his [Extrusion Test Structure](https://www.printables.com/model/342075-extrusion-test-structure).*
|
||||
- *ZV Input Shaping is inspired by [Marlin Input Shaping](https://marlinfw.org/docs/features/input_shaping.html) and [Ringing Tower 3D STL](https://marlinfw.org/assets/stl/ringing_tower.stl).*
|
||||
- *ChatGPT* ;)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,23 +1,38 @@
|
|||
OrcaSlicer use `M141/M191` command to control active chamber heater.
|
||||
# Chamber Temperature Control
|
||||
|
||||
If `Activate temperature control` is checked, OrcaSlicer will insert `M191` command at the beginning of the gcode(before `Machine G-code`).
|
||||

|
||||
*Note: If the machine is equipped with an auxiliary fan, OrcaSlicer will automatically activate the fan during the heating period to help circulate air in the chamber.*
|
||||
OrcaSlicer use `M141/M191` command to control active chamber heater.
|
||||
|
||||
If your Filament's `Activate temperature control` and your printer `Support control chamber temperature` option are checked , OrcaSlicer will insert `M191` command at the beginning of the gcode (before `Machine G-code`).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
There are two chamber temperature variables available that we can use in `Machine G-code` to control the chamber temperature, if you prefer:
|
||||
To access the chamber temperature set in the first filament, use:
|
||||
`M191 S{chamber_temperature[0]}`
|
||||
To use the overall chamber temperature, which is the highest chamber temperature set across all filaments, use:
|
||||
`M191 S{overall_chamber_temperature}`
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> If the machine is equipped with an auxiliary fan, OrcaSlicer will automatically activate the fan during the heating period to help circulate air in the chamber.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Chamber Temperature Variables in Machine G-code
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------Klipper--------------------------
|
||||
If you are using Klipper, you can define these macros to control the active chamber heater.
|
||||
Bellow is a reference configuration for Klipper.
|
||||
*Note: Don't forget to change the pin name/values to the actual values you are using in the configuration*
|
||||
You can use chamber temperature variables in your `Machine G-code` to control the chamber temperature manually, if desired:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
- To set the chamber temperature to the value specified for the first filament:
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M191 S{chamber_temperature[0]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- To set the chamber temperature to the highest value specified across all filaments:
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M191 S{overall_chamber_temperature}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Klipper
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Klipper, you can define these macros to control the active chamber heater.
|
||||
Bellow is a reference configuration for Klipper.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Don't forget to change the pin name/values to the actual values you are using in the configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
[heater_generic chamber_heater]
|
||||
heater_pin:PB10
|
||||
max_power:1.0
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,7 +40,7 @@ max_power:1.0
|
|||
sensor_type:NTC 100K MGB18-104F39050L32
|
||||
sensor_pin:PA1
|
||||
control = pid
|
||||
pid_Kp = 63.418
|
||||
pid_Kp = 63.418
|
||||
pid_ki = 0.960
|
||||
pid_kd = 1244.716
|
||||
min_temp:0
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,5 +63,4 @@ gcode:
|
|||
TEMPERATURE_WAIT SENSOR="heater_generic chamber_heater" MINIMUM={s-1} MAXIMUM={s+1}
|
||||
M117 Chamber at target temperature
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
48
doc/Home.md
|
|
@ -1,40 +1,68 @@
|
|||
# Welcome to the OrcaSlicer WIKI!
|
||||
|
||||
Orca slicer is a powerful open source slicer for FFF (FDM) 3D Printers. This wiki page aims to provide an detailed explanation of the slicer settings, how to get the most out of them as well as how to calibrate and setup your printer.
|
||||
Orca slicer is a powerful open source slicer for FFF (FDM) 3D Printers. This wiki page aims to provide an detailed explanation of the slicer settings, how to get the most out of them as well as how to calibrate and setup your printer.
|
||||
|
||||
The Wiki is work in progress so bear with us while we get it up and running!
|
||||
- [Print Settings, Tips and Tricks](#print-settings-tips-and-tricks)
|
||||
- [Quality Settings](#quality-settings)
|
||||
- [Speed Settings](#speed-settings)
|
||||
- [Multi material](#multi-material)
|
||||
- [Printer Settings](#printer-settings)
|
||||
- [Printer Calibration](#printer-calibration)
|
||||
- [Developer Section](#developer-section)
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> The Wiki is **Work In Progress** so bear with us while we get it up and running!
|
||||
|
||||
## Print Settings, Tips and Tricks
|
||||
|
||||
## Print Settings, Tips and Tricks (Work In Progress)
|
||||
The below sections provide a detailed settings explanation as well as tips and tricks in setting these for optimal print results.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quality Settings
|
||||
|
||||
- [Layer Height Settings](quality_settings_layer_height)
|
||||
- [Line Width Settings](quality_settings_line_width)
|
||||
- [Seam Settings](quality_settings_seam)
|
||||
- [Precise wall](Precise-wall)
|
||||
- [Precise Z height](precise-z-height)
|
||||
- [STL Transformation](stl-transformation)
|
||||
|
||||
### Speed Settings
|
||||
|
||||
- [Extrusion rate smoothing](extrusion-rate-smoothing)
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi material
|
||||
|
||||
- [Single Extruder Multimaterial](semm)
|
||||
|
||||
### Printer Settings:
|
||||
### Printer Settings
|
||||
|
||||
- [Air filtration/Exhaust fan handling](air-filtration)
|
||||
- [Auxiliary fan handling](Auxiliary-fan)
|
||||
- [Chamber temperature control](chamber-temperature)
|
||||
- [Adaptive Bed Mesh](adaptive-bed-mesh)
|
||||
- [Using different bed types in Orca](bed-types)
|
||||
- [Pellet Printers (pellet flow coefficient)](pellet-flow-coefficient)
|
||||
- [Fill Patterns](fill-patterns)
|
||||
|
||||
## Printer Calibration
|
||||
The guide below takes you through the key calibration tests in Orca - flow rate, pressure advance, print temperature, retraction, tolerances and maximum volumetric speed
|
||||
- [Calibration Guide](./Calibration)
|
||||
- [Adaptive Pressure Advance Guide](adaptive-pressure-advance)
|
||||
|
||||
The [Calibration Guide](Calibration) outlines Orca’s key calibration tests and their suggested order of execution.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Temperature](temp-calib)
|
||||
- [Flow Rate](flow-rate-calib)
|
||||
- [Pressure Advance](pressure-advance-calib)
|
||||
- [Adaptive Pressure Advance Guide](adaptive-pressure-advance-calib)
|
||||
- [Retraction](retraction-calib)
|
||||
- [Tolerance](tolerance-calib)
|
||||
- Advanced:
|
||||
- [Volumetric Speed](volumetric-speed-calib)
|
||||
- [Cornering (Jerk & Junction Deviation)](cornering-calib)
|
||||
- [Input Shaping](input-shaping-calib)
|
||||
|
||||
## Developer Section
|
||||
- [How to build Orca Slicer](./How-to-build)
|
||||
|
||||
- [How to build Orca Slicer](How-to-build)
|
||||
- [Localization and translation guide](Localization_guide)
|
||||
- [Developer Reference](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/doc/developer-reference/Home.md)
|
||||
- [How to create profiles](./How-to-create-profiles)
|
||||
- [Developer Reference](Developers-Home)
|
||||
- [How to create profiles](How-to-create-profiles)
|
||||
- [How to contribute to the wiki](How-to-wiki)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,11 +1,193 @@
|
|||
# How to compile
|
||||
- Windows 64-bit
|
||||
- Tools needed: Visual Studio 2019, Cmake, git, Strawberry Perl.
|
||||
- Run `build_release.bat` in `x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019`
|
||||
# How to Build
|
||||
|
||||
- Mac 64-bit
|
||||
- Tools needed: Xcode, Cmake, git, gettext
|
||||
- run `build_release_macos.sh`
|
||||
## Windows 64-bit
|
||||
|
||||
- Ubuntu
|
||||
- run `BuildLinux.sh -udisr`
|
||||
This guide is for building your Visual Studio 2022 solution for OrcaSlicer on Windows 64-bit.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tools Required
|
||||
|
||||
- [Visual Studio 2022](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/vs/) or Visual Studio 2019
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
winget install --id=Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.Professional -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [CMake (version 3.31)](https://cmake.org/) — **⚠️ version 3.31.x is mandatory**
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
winget install --id=Kitware.CMake -v "3.31.6" -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [Strawberry Perl](https://strawberryperl.com/)
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
winget install --id=StrawberryPerl.StrawberryPerl -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [Git](https://git-scm.com/)
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
winget install --id=Git.Git -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [git-lfs](https://git-lfs.com/)
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
winget install --id=GitHub.GitLFS -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> GitHub Desktop (optional): A GUI for Git and Git LFS, which already includes both tools.
|
||||
> ```shell
|
||||
> winget install --id=GitHub.GitHubDesktop -e
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
|
||||
### Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone the repository:
|
||||
- If using GitHub Desktop clone the repository from the GUI.
|
||||
- If using the command line:
|
||||
1. Clone the repository:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Run lfs to download tools on Windows:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git lfs pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Open the appropriate command prompt:
|
||||
- For Visual Studio 2019:
|
||||
Open **x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019** and run:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
build_release.bat
|
||||
```
|
||||
- For Visual Studio 2022:
|
||||
Open **x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022** and run:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
build_release_vs2022.bat
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. If successful, you will find the VS 2022 solution file in:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
build\OrcaSlicer.sln
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Make sure that CMake version 3.31.x is actually being used. Run `cmake --version` and verify it returns a **3.31.x** version.
|
||||
> If you see an older version (e.g. 3.29), it's likely due to another copy in your system's PATH (e.g. from Strawberry Perl).
|
||||
> You can run where cmake to check the active paths and rearrange your System Environment Variables > PATH, ensuring the correct CMake (e.g. C:\Program Files\CMake\bin) appears before others like C:\Strawberry\c\bin.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> If the build fails, try deleting the `build/` and `deps/build/` directories to clear any cached build data. Rebuilding after a clean-up is usually sufficient to resolve most issues.
|
||||
|
||||
## macOS 64-bit
|
||||
|
||||
### Tools Required
|
||||
|
||||
- Xcode
|
||||
- CMake (version 3.31.x is mandatory)
|
||||
- Git
|
||||
- gettext
|
||||
- libtool
|
||||
- automake
|
||||
- autoconf
|
||||
- texinfo
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> You can install most of them by running:
|
||||
> ```shell
|
||||
> brew install gettext libtool automake autoconf texinfo
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
|
||||
Homebrew currently only offers the latest version of CMake (e.g. **4.X**), which is not compatible. To install the required version **3.31.X**, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download CMake **3.31.7** from: [https://cmake.org/download/](https://cmake.org/download/)
|
||||
2. Install the application (drag it to `/Applications`).
|
||||
3. Add the following line to your shell configuration file (`~/.zshrc` or `~/.bash_profile`):
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
export PATH="/Applications/CMake.app/Contents/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Restart the terminal and check the version:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
cmake --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Make sure it reports a **3.31.x** version.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> If you've recently upgraded Xcode, be sure to open Xcode at least once and install the required macOS build support.
|
||||
|
||||
### Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone the repository:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer
|
||||
cd OrcaSlicer
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Build the application:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
./build_release_macos.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Open the application:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
open build/arm64/OrcaSlicer/OrcaSlicer.app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Debugging in Xcode
|
||||
|
||||
To build and debug directly in Xcode:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open the Xcode project:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
open build/arm64/OrcaSlicer.xcodeproj
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. In the menu bar:
|
||||
- **Product > Scheme > OrcaSlicer**
|
||||
- **Product > Scheme > Edit Scheme...**
|
||||
- Under **Run > Info**, set **Build Configuration** to `RelWithDebInfo`
|
||||
- Under **Run > Options**, uncheck **Allow debugging when browsing versions**
|
||||
- **Product > Run**
|
||||
|
||||
## Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Docker (Recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
- Docker
|
||||
- Git
|
||||
|
||||
#### Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer && cd OrcaSlicer && ./DockerBuild.sh && ./DockerRun.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> To troubleshoot common Docker-related errors, refer to the comments in
|
||||
> ```shell
|
||||
> DockerRun.sh
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
|
||||
## Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
All required dependencies will be installed automatically by the provided shell script, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- libmspack-dev
|
||||
- libgstreamerd-3-dev
|
||||
- libsecret-1-dev
|
||||
- libwebkit2gtk-4.0-dev
|
||||
- libosmesa6-dev
|
||||
- libssl-dev
|
||||
- libcurl4-openssl-dev
|
||||
- eglexternalplatform-dev
|
||||
- libudev-dev
|
||||
- libdbus-1-dev
|
||||
- extra-cmake-modules
|
||||
- libgtk2.0-dev
|
||||
- libglew-dev
|
||||
- cmake
|
||||
- git
|
||||
- texinfo
|
||||
|
||||
### Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo ./BuildLinux.sh -u # Install dependencies
|
||||
./BuildLinux.sh -dsi # Build OrcaSlicer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,10 +1,13 @@
|
|||
# Guide: Develop Profiles for OrcaSlicer
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help you develop profiles for OrcaSlicer.
|
||||
|
||||
## High-level Overview
|
||||
|
||||
OrcaSlicer uses JSON files to store profiles. There are four types of profiles:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Printer model (type `machine_model`). Example: `Orca 3D Fuse1.json`
|
||||
2. Printer variant (type `machine`). Example: `Orca 3D Fuse1 0.2 nozzle.json`
|
||||
3. Filament (type `filament`). Example: `Generic PLA @Orca 3D Fuse1@.json`
|
||||
|
|
@ -15,6 +18,7 @@ Additionally, there is an overall meta file for each vendor (`Orca 3D.json`).
|
|||
For easier understanding, let's consider a scenario with a printer manufacturer called `Orca 3D`. The manufacturer offers one printer model called `Fuse 1`, which supports 0.2/0.4/0.6/0.8mm nozzles and common market filaments.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case:
|
||||
|
||||
- Vendor profile: `Orca 3D`
|
||||
- Printer profile: `Orca 3D Fuse1`
|
||||
- Printer variant profile: `Orca 3D Fuse1 0.4 nozzle`
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,39 +27,54 @@ In this case:
|
|||
|
||||
The profile name should be same as the filename without the `.json` extension in principal.
|
||||
Naming conventions:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Vendor profile: `vendor_name.json`
|
||||
2. Printer profile: `vendor_name` + `printer_name` + `.json`
|
||||
3. Printer variant profile: `vendor_name` + `printer_variant_name` + `.json` (where `printer_variant_name` typically includes `printer_name` + `nozzle_diameter`)
|
||||
4. Filament profile: `filament_vendor_name` + `filament_name` + " @" + `vendor_name` + `printer_name`/`printer_variant_name` + `.json`
|
||||
5. Process profile: `layer_height` + `preset_name` + " @" + `vendor_name` + `printer_name`/`printer_variant_name` + `.json` (`preset_name` typically includes "standard," "fine," "fast," "draft," etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
## File Structure and Templates
|
||||
|
||||
A typical file structure for a vendor:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Profiles should be structured in the following way under the OrcaSlicer installation directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```plaintext
|
||||
resources\profiles\
|
||||
- Orca 3D.json
|
||||
- Orca 3D\
|
||||
- machine\
|
||||
- Orca 3D Fuse1.json
|
||||
- Orca 3D Fuse1 0.2 nozzle.json
|
||||
- Orca 3D Fuse1 0.4 nozzle.json
|
||||
- process\
|
||||
- 0.10mm Standard @Orca 3D Fuse1 0.2.json
|
||||
- 0.20mm Standard @Orca 3D Fuse1 0.4.json
|
||||
- filament\
|
||||
- Generic PLA @Orca 3D Fuse1@.json
|
||||
├── Orca 3D.json
|
||||
└── Orca 3D\
|
||||
├── machine\
|
||||
│ ├── Orca 3D Fuse1.json
|
||||
│ ├── Orca 3D Fuse1 0.2 nozzle.json
|
||||
│ └── Orca 3D Fuse1 0.4 nozzle.json
|
||||
├── process\
|
||||
│ ├── 0.10mm Standard @Orca 3D Fuse1 0.2.json
|
||||
│ └── 0.20mm Standard @Orca 3D Fuse1 0.4.json
|
||||
└── filament\
|
||||
└── Generic PLA @Orca 3D Fuse1@.json
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Use short vendor names in filenames to avoid excessive length.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE 1**: Use short vendor names in filenames to avoid excessive length.
|
||||
**NOTE 2**: Filament profiles are **optional**. Create them only if the vendor has specifically tuned profiles for the given printer. See [Filament profiles](#filament-profiles) for details.
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Filament profiles are **optional**. Create them only if the vendor has specifically tuned profiles for the given printer. See [Filament profiles](#filament-profiles) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
Template files for profiles are available in:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
OrcaSlicer\resources\profiles_template\Template
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These templates can be used as a starting point for new printer, filament, and process profiles.
|
||||
|
||||
## Filament Profiles
|
||||
|
||||
OrcaSlicer features a global filament library called `OrcaFilamentLibrary`, which is automatically available for all printers. It includes generic filaments like `Generic PLA @System` and `Generic ABS @System` etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Printer vendors can override specific filaments in the global library for certain printer models by creating new filament profiles.
|
||||
Printer vendors can override specific filaments in the global library for certain printer models by creating new filament profiles.
|
||||
|
||||
Relationship diagram:
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
graph TD;
|
||||
OrcaFilamentLibrary-->Orca_3D_filament;
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,9 +82,11 @@ graph TD;
|
|||
OrcaFilamentLibrary-->Vendor_B_filament;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE**: Create new filament profiles only if you have truly specifically tuned the filament for the given printer. Otherwise, use the global library. The global library has a better chance to receive optimizations and updates from OrcaSlicer contributors, which will benefit users of all printers.
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Create new filament profiles only if you have truly specifically tuned the filament for the given printer. Otherwise, use the global library. The global library has a better chance to receive optimizations and updates from OrcaSlicer contributors, which will benefit users of all printers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding Filament Profiles to the Global Library
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will discuss how to add a new filament profile into the global library.
|
||||
If you want to add a new generic profile into the global library, you need to create a new file in the `resources\profiles\OrcaFilamentLibrary\filament` folder. If a base type already exists in the global library, you can use this file as a base profile by inheriting it.
|
||||
The following sample JSON file shows how to create a new generic filament profile `Generic PLA-GF @System` in the global library.
|
||||
|
|
@ -107,11 +128,13 @@ The following sample JSON file shows how to create a new generic filament profil
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. The last step is to validate the newly added filament profiles. You can run OrcaSlicer to verify if the filament you just added is available and usable. You can also use the [Orca profile validator](https://github.com/SoftFever/Orca_tools/releases/tag/1) tool to help debug any errors. **NOTE**: You need to delete the `%appdata%/OrcaSlicer/system` folder to force OrcaSlicer to reload your lastest changes.
|
||||
3. The last step is to validate the newly added filament profiles see [Validate Profiles](#validate-profiles).
|
||||
|
||||
The process is the same if you want to add a new brand filament profile into the global library. You need to create a new file in the `resources\profiles\OrcaFilamentLibrary\filament\brand_name` folder. The only difference is that you should put the file into the brand's own subfolder.`resources\profiles\OrcaFilamentLibrary\filament\brand_name`.
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> If the filament is compatible with AMS, ensure that the `filament_id` value **does not exceed 8 characters** to maintain AMS compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding Filament Profiles to Printer Vendor Library
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will discuss how to add a new filament profile for a certain vendor.
|
||||
If you want to add a new filament profile, whether it's a brand new profile or a specialized version of a global filament profile for a given printer, you need to create a new file in the `resources\profiles\vendor_name\filament` folder. If a base type already exists in the global library, you can use this file as a base profile by inheriting it.
|
||||
Below is a sample JSON file showing how to create a specialized `Generic ABS` filament profile for the ToolChanger printer.
|
||||
|
|
@ -170,11 +193,224 @@ Please note that here we must leave the compatible_printers field non-empty, unl
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Process Profiles
|
||||
WIP...
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> If the filament is compatible with AMS, ensure that the `filament_id` value **does not exceed 8 characters** to maintain AMS compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
## Printer Profiles
|
||||
WIP...
|
||||
## Process Profiles
|
||||
|
||||
Process profiles define print quality and behavior. They follow a structure similar to filament profiles:
|
||||
|
||||
- A common base file, e.g., `fdm_process_common.json`, acts as the parent.
|
||||
- Vendor-specific process profiles should inherit from the base using the `inherits` field.
|
||||
- Profiles are stored under:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resources\profiles\vendor_name\process\
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **There are no global process profiles**.
|
||||
- Each process profile includes a `"compatible_printers"` field with an array of compatible printer variant names.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "process",
|
||||
"name": "0.10mm Standard @ExampleVendor Printer 0.2",
|
||||
"inherits": "fdm_process_common",
|
||||
"from": "system",
|
||||
"instantiation": "true",
|
||||
"compatible_printers": [
|
||||
"ExampleVendor Printer 0.2 nozzle"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Printer Model Profiles
|
||||
|
||||
- Printer model profiles (type `machine_model`) describe the general printer information.
|
||||
- Example fields: `nozzle_diameter`, `bed_model`, `bed_texture`, `model_id`, etc.
|
||||
- Stored in:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
resources\profiles\vendor_name\machine\
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Each vendor's folder may contain an image named:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
[machine_model_list.name]_cover.png
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This image will be used in the UI.
|
||||
|
||||
Example model profile:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "machine_model",
|
||||
"name": "Example M5",
|
||||
"nozzle_diameter": "0.2;0.25;0.4;0.6",
|
||||
"bed_model": "M5-Example-bed.stl",
|
||||
"bed_texture": "M5-Example-texture.svg",
|
||||
"model_id": "V1234",
|
||||
"family": "Example",
|
||||
"machine_tech": "FFF",
|
||||
"default_materials": "Example Generic PLA;Example Generic PETG"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Printer Variant Profiles
|
||||
WIP...
|
||||
|
||||
- Printer variants (type `machine`) define specific nozzle configurations and mechanical details.
|
||||
- Each variant must inherit from a common base like `fdm_machine_common.json`.
|
||||
- Must list the compatible nozzle diameter in the `nozzle_diameter` array.
|
||||
- Example fields include `printer_model`, `printer_variant`, `default_print_profile`, `printable_area`, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Example variant profile:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "machine",
|
||||
"name": "Example M5 0.2 nozzle",
|
||||
"inherits": "fdm_machine_common",
|
||||
"from": "system",
|
||||
"setting_id": "GM001",
|
||||
"instantiation": "true",
|
||||
"nozzle_diameter": ["0.2"],
|
||||
"printer_model": "Example M5",
|
||||
"printer_variant": "0.2",
|
||||
"default_filament_profile": ["Example Generic PLA"],
|
||||
"default_print_profile": "0.10mm Standard 0.2mm nozzle @Example",
|
||||
"printable_area": ["0x0", "235x0", "235x235", "0x235"],
|
||||
"nozzle_type": "brass"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
|
||||
- The `model` directory under the vendor folder is intended to behave similarly to `machine` profiles.
|
||||
- Used for additional printer-related 3D models or definitions, stored at:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
resources\profiles\vendor_name\model\
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Vendor Meta File
|
||||
|
||||
Each vendor must include a JSON file in the `resources\profiles` directory, named `vendor_name.json`. This file lists all available models, variants, processes, and filaments:
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "ExampleVendor",
|
||||
"version": "01.00.00.00",
|
||||
"force_update": "1",
|
||||
"description": "Example configuration",
|
||||
"machine_model_list": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Example M5",
|
||||
"sub_path": "machine/Example M5.json"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"machine_list": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "fdm_machine_common",
|
||||
"sub_path": "machine/fdm_machine_common.json"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"process_list": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "fdm_process_common",
|
||||
"sub_path": "process/fdm_process_common.json"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"filament_list": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "fdm_filament_common",
|
||||
"sub_path": "filament/fdm_filament_common.json"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Validate Profiles
|
||||
|
||||
You can validate your profiles using both the **OrcaSlicer profile validator** and the **Python validation script**. These tools are designed to check different aspects of the profiles, so both should be executed and pass without errors to ensure full compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> **✅ Recommendation:** Always run **both** the OrcaSlicer validator and the Python script to ensure all aspects of the profiles are valid.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. OrcaSlicer Profile Validator
|
||||
|
||||
You can run OrcaSlicer to verify if the filament you just added is available and usable. You can also use the [Orca profile validator](https://github.com/SoftFever/Orca_tools/releases/tag/1) tool to help debug any errors.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> You need to delete the `%appdata%/OrcaSlicer/system` folder to force OrcaSlicer to reload your lastest changes.
|
||||
|
||||
The process is the same if you want to add a new brand filament profile into the global library. You need to create a new file in the `resources\profiles\OrcaFilamentLibrary\filament\brand_name` folder. The only difference is that you should put the file into the brand's own subfolder.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
-h [ --help ] help
|
||||
-p [ --path ] arg profile folder
|
||||
-v [ --vendor ] arg Vendor name. Optional, all profiles present in the folder will be validated if not specified
|
||||
-l [ --log_level ] arg (=2) Log level. Optional, default is 2 (warning). Higher values produce more detailed logs.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
./OrcaSlicer_profile_validator -p ~/codes/OrcaSlicer/resources/profiles -l 2 -v Custom
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample result with errors
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PS D:\codes\OrcaSlicer> ."D:/codes/OrcaSlicer/build/src/Release/OrcaSlicer_profile_validator.exe" --path d:\codes\OrcaSlicer\resources\profiles -l 2 -v Custom
|
||||
[2024-02-28 21:23:06.102138] [0x0000a4e8] [error] Slic3r::ConfigBase::load_from_json: parse d:\codes\OrcaSlicer\resources\profiles/Custom/machine/fdm_klipper_common.json got a nlohmann::detail::parse_error, reason = [json.exception.parse_error.101] parse error at line 9, column 38: syntax error while parsing object - unexpected string literal; expected '}'
|
||||
...
|
||||
Validation failed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample result with success
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PS D:\codes\OrcaSlicer\build\src\RelWithDebInfo> ."D:/codes/OrcaSlicer/build/src/Release/OrcaSlicer_profile_validator.exe" --path d:\codes\OrcaSlicer\resources\profiles -l 2 -v Custom
|
||||
Validation completed successfully
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Use `OrcaSlicer_profile_validator` on Ubuntu and `OrcaSlicer_profile_validator.exe` on Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Python Profile Validation Script
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the Orca validator, you should run the `orca_extra_profile_check.py` script. This script performs additional checks like:
|
||||
|
||||
- Validation of `compatible_printers` in filament profiles
|
||||
- Consistency of filament names
|
||||
- Validation of default materials in machine profiles (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example command
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python ./orca_extra_profile_check.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also enable or disable specific checks:
|
||||
|
||||
- `--vendor` (optional): checks only the specified vendor. If omitted, all vendors are checked.
|
||||
- `--check-filaments` (enabled by default): checks `compatible_printers` fields in filament profiles
|
||||
- `--check-materials`: checks default material names in machine profiles
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample usage with all checks enabled
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python ./orca_extra_profile_check.py --vendor="vendor_name" --check-filaments --check-materials
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The script will output the number of errors found and exit with a non-zero status code if any issues are detected.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
246
doc/How-to-wiki.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,246 @@
|
|||
# How to Contribute to the Wiki
|
||||
|
||||
This guide explains how to contribute to the Orca Slicer wiki.
|
||||
|
||||
Orca Slicer uses GitHub's wiki feature, which allows users and developers to create and edit documentation collaboratively.
|
||||
|
||||
We encourage all developers and users to contribute to the wiki by updating existing pages and adding new content. This helps keep the documentation up-to-date and useful for everyone.
|
||||
|
||||
When developing new features, please consider updating the wiki to reflect these changes. This ensures that users have access to the latest information and can make the most of the features.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wiki Structure](#wiki-structure)
|
||||
- [Home](#home)
|
||||
- [Index and Navigation](#index-and-navigation)
|
||||
- [File Naming and Organization](#file-naming-and-organization)
|
||||
- [Formatting and Style](#formatting-and-style)
|
||||
- [Markdown Formatting](#markdown-formatting)
|
||||
- [Alerts and Callouts](#alerts-and-callouts)
|
||||
- [Images](#images)
|
||||
- [Image Naming](#image-naming)
|
||||
- [Image Placement](#image-placement)
|
||||
- [Linking Images](#linking-images)
|
||||
- [Examples](#examples)
|
||||
- [Avoid the Following](#avoid-the-following)
|
||||
- [Resize Images](#resize-images)
|
||||
- [Image Cropping and Highlighting](#image-cropping-and-highlighting)
|
||||
- [Recommended Formats](#recommended-formats)
|
||||
- [Structuring Content](#structuring-content)
|
||||
- [Commands and Code Blocks](#commands-and-code-blocks)
|
||||
- [External Links](#external-links)
|
||||
|
||||
## Wiki Structure
|
||||
|
||||
Each wiki page is a Markdown file located in the `doc` directory of the repository. The wiki is organized into various sections, each covering different areas of the project.
|
||||
|
||||
### Home
|
||||
|
||||
The starting point of the Orca Slicer wiki is the **Home** page. From there, you can navigate to different sections and topics related to the project.
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a new page or section, be sure to link it from the Home page under the appropriate category.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Print Settings:** Detailed explanations of print settings, tips, and tricks for optimizing print quality.
|
||||
- **Printer Calibration:** Step-by-step calibration tests in Orca Slicer, including how to interpret the results.
|
||||
- **Developer Section:** Information for developers and contributors on building Orca Slicer, localization, and developer resources.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Index and Navigation
|
||||
|
||||
Github Wiki uses the name of the files as identifiers for the pages. To link to a page, use the file name without the `.md` extension.
|
||||
If the file is inside a subdirectory, dont include the subdirectory in the link. Instead, link directly to the file from the Home page.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you create a new page `doc/calibration/flow-rate-calib.md`, link it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
[Calibration Guide](Calibration)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For pages with extensive content, it's helpful to include a table of contents at the beginning. This allows users to quickly find and access different sections of the page.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
- [Wiki Structure](#wiki-structure)
|
||||
- [Home](#home)
|
||||
- [Index and Navigation](#index-and-navigation)
|
||||
- [File Naming and Organization](#file-naming-and-organization)
|
||||
- [Formatting and Style](#formatting-and-style)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> If you're adding a new section, follow the existing structure and ensure it doesn't already fit within an existing category. Link it from the Home page accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
### File Naming and Organization
|
||||
|
||||
When creating new pages, follow these file naming conventions:
|
||||
|
||||
- Use unique file names to avoid conflicts.
|
||||
- Use descriptive names that reflect the page's content.
|
||||
- Use kebab-case for filenames (e.g., `How-to-wiki.md`).
|
||||
- If the page belongs to a specific section, include the section name in the file name. For example, calibration pages should end with `-calib.md` (e.g., `flow-rate-calib.md`, `pressure-advance-calib.md`).
|
||||
- Place files in the appropriate subdirectory when applicable (e.g., `doc/calibration/` for calibration-related content).
|
||||
|
||||
## Formatting and Style
|
||||
|
||||
Please adhere to the following style and formatting conventions when contributing to the wiki.
|
||||
|
||||
### Markdown Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
The wiki uses standard Markdown syntax for formatting and aims to maintain a consistent style across all pages. Avoid using raw HTML tags and prefer Markdown formatting instead.
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure your indentation is consistent, especially for code blocks and lists.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [GitHub Markdown Guide](https://guides.github.com/features/mastering-markdown/) for more information on Markdown syntax.
|
||||
|
||||
### Alerts and Callouts
|
||||
|
||||
To add alerts or notes, use GitHub’s Markdown alert syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Useful information that users should know, even when skimming content.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Helpful advice for doing things better or more easily.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Key information users need to know to achieve their goal.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Urgent info that needs immediate user attention to avoid problems.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!CAUTION]
|
||||
> Advises about risks or negative outcomes of certain actions.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Useful information that users should know, even when skimming content.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Helpful advice for doing things better or more easily.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Key information users need to know to achieve their goal.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Urgent info that needs immediate user attention to avoid problems.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!CAUTION]
|
||||
> Advises about risks or negative outcomes of certain actions.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [GitHub Alert Guide](https://docs.github.com/get-started/writing-on-github/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github/basic-writing-and-formatting-syntax#alerts) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## Images
|
||||
|
||||
Images are encouraged to enhance the clarity and quality of the wiki content. They help illustrate concepts, provide examples, and improve readability.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!CAUTION]
|
||||
> Do not use images from third-party sources unless you have the proper permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Image Naming
|
||||
|
||||
- Use clear, descriptive filenames that reflect the image content.
|
||||
- For section-specific images, include the section name or initials. For example, images related to Pressure Advance could be named `pa-[description].png`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Image Placement
|
||||
|
||||
- General images should be placed in the `doc/images/` directory.
|
||||
- Section-specific images should be stored in their corresponding subdirectories (e.g., `doc/images/calibration/` for calibration content).
|
||||
|
||||
### Linking Images
|
||||
|
||||
Always use raw GitHub URLs for image links to ensure correct display:
|
||||
|
||||
Format = `![[filename]](` + Base URL + filename.extension + Raw tag + `)`
|
||||
|
||||
- Base URL:
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/doc/images/
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Raw tag:
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
?raw=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
- For an image in `doc/images/` named `example.png`:
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||

|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For an image in a subdirectory like `doc/images/calibration/pa-example.svg`:
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||

|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> New or Moved Images will not appear in the preview until the Pull Request is merged. Double-check your paths.
|
||||
> If you are changing an image path, ensure all links to that image are updated accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Avoid the Following
|
||||
|
||||
- Relative paths
|
||||
- GitHub Assets, user content, or user-images URLs
|
||||
- External image links from unreliable or temporary platforms
|
||||
- Images containing personal or sensitive information
|
||||
- Using images for content that can be expressed in text, such as equations or code—use Markdown syntax or Mermaid/Math formatting instead.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> When contributing section-specific images, follow the naming conventions and directory structure.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Resize Images
|
||||
|
||||
Avoid the resize of images and let the Wiki handle it automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
If resizing is necessary (e.g., for thumbnails), use the following syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
HTML Format = `<img src="` + Base URL + filename.extension + Raw tag + `" alt="` + filename + `"` + size limit.
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/doc/images/InputShaping/IS_damp_marlin_print_measure.jpg?raw=true" alt="Input_Shaping" height="200">
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Image Cropping and Highlighting
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure clarity:
|
||||
|
||||
- Crop images to focus on relevant areas.
|
||||
- Use annotations like arrows or shapes (circles, rectangles) to highlight key parts—but avoid overloading the image.
|
||||
|
||||
### Recommended Formats
|
||||
|
||||
- **JPG:** Suitable for photographs. Avoid for images with text or fine detail due to compression artifacts.
|
||||
- **PNG:** Ideal for screenshots or images with transparency. Ensure sufficient contrast for light and dark modes.
|
||||
- **SVG:** Preferred when possible. SVGs support theme adaptation (light/dark mode), making them ideal for icons and diagrams.
|
||||
|
||||
## Structuring Content
|
||||
|
||||
Each wiki page should have a clear objective, which helps determine the structure of the content. After a brief introduction, use one of the following formats:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Step-by-Step Guide:** Organize content into sections and subsections for tasks requiring sequential actions (e.g., calibration procedures).
|
||||
- **GUI-Based Reference:** If sequence isn’t crucial, structure the content following Orca Slicer’s GUI. This format works well for configurable settings or feature overviews.
|
||||
- Example: Explain **Layer Height** before **Initial Layer Height**, as the former applies globally while the latter is specific to the first layer.
|
||||
|
||||
## Commands and Code Blocks
|
||||
|
||||
When adding commands or code blocks please use the [Code Block with Syntax Highlighting feature of Markdown](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/working-with-advanced-formatting/creating-and-highlighting-code-blocks#syntax-highlighting).
|
||||
|
||||
- Use triple backticks (```) to enclose code blocks.
|
||||
- Specify the language for proper highlighting and readability.
|
||||
|
||||
````markdown
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "value"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"key": "value"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## External Links
|
||||
|
||||
Be careful when linking to external resources. Ensure that the links are relevant and reliable.
|
||||
Papers, articles, and other resources should be cited properly.
|
||||
|
|
@ -2,26 +2,28 @@
|
|||
|
||||
The purpose of this guide is to describe how to contribute to the Orca Slicer translations. We use GNUgettext for extracting string resources from the project and PoEdit for editing translations.
|
||||
|
||||
Those can be downloaded here:
|
||||
- https://sourceforge.net/directory/os:windows/?q=gnu+gettext GNUgettext package contains a set of tools to extract strings from the source code and to create the translation Catalog.
|
||||
- https://poedit.net PoEdit provides good interface for the translators.
|
||||
Those can be downloaded here:
|
||||
|
||||
- https://sourceforge.net/directory/os:windows/?q=gnu+gettext GNUgettext package contains a set of tools to extract strings from the source code and to create the translation Catalog.
|
||||
- https://poedit.net PoEdit provides good interface for the translators.
|
||||
|
||||
After GNUgettext is installed, it is recommended to add the path to gettext/bin to PATH variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Full manual for GNUgettext can be seen here: http://www.gnu.org/software/gettext/manual/gettext.html
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 1. How do I add a translation or fix an existing translation
|
||||
|
||||
1. Get PO-file 'OrcaSlicer_xx.pot' from corresponding sub-folder here:
|
||||
https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/tree/master/localization/i18n
|
||||
https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/tree/master/localization/i18n
|
||||
2. Open this file in PoEdit as "Edit a translation"
|
||||
3. Apply your corrections to the translation
|
||||
4. Push changed OrcaSlicer_xx.po into the original folder
|
||||
5. copy OrcaSlicer_xx.mo into resources/i18n/xx and rename it to OrcaSlicer.mo, then push the changed file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 2. How do I add a new language support
|
||||
|
||||
1. Get file OrcaSlicer.pot here :
|
||||
https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/tree/master/localization/i18n
|
||||
https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/tree/master/localization/i18n
|
||||
2. Open it in PoEdit for "Create new translation"
|
||||
3. Select Translation Language (for example French).
|
||||
4. As a result you will have fr.po - the file containing translation to French.
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,24 +32,28 @@ Notice. When the translation is complete you need to:
|
|||
- Click "Save file" button. OrcaSlicer_fr.mo will be created immediately
|
||||
- Bambu_Studio_fr.po needs to be copied into the sub-folder fr of https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/tree/master/localization/i18n, and be pushed
|
||||
- copy OrcaSlicer_xx.mo into resources/i18n/xx and rename it to OrcaSlicer.mo, then push the changed file.
|
||||
( name of folder "fr" means "French" - the translation language).
|
||||
( name of folder "fr" means "French" - the translation language).
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 3. How do I add a new text resource when implementing a feature to Orca Slicer
|
||||
|
||||
Each string resource in Orca Slicer available for translation needs to be explicitly marked using L() macro like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```C++
|
||||
auto msg = L("This message to be localized")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To get translated text use one of needed macro/function (`_(s)` or `_CHB(s)` ).
|
||||
If you add new file resource, add it to the list of files containing macro `L()`
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 4. How do I use GNUgettext to localize my own application taking Orca Slicer as an example
|
||||
|
||||
1. For convenience create a list of files with this macro `L(s)`. We have
|
||||
https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/blob/master/localization/i18n/list.txt.
|
||||
1. For convenience create a list of files with this macro `L(s)`. We have
|
||||
https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/blob/master/localization/i18n/list.txt.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create template file(*.POT) with GNUgettext command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
xgettext --keyword=L --add-comments=TRN --from-code=UTF-8 --debug -o OrcaSlicer.pot -f list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
xgettext --keyword=L --add-comments=TRN --from-code=UTF-8 --debug -o OrcaSlicer.pot -f list.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use flag `--from-code=UTF-8` to specify that the source strings are in UTF-8 encoding
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,38 +62,37 @@ https://github.com/softfever/OrcaSlicer/blob/master/localization/i18n/list.txt.
|
|||
3. Create PO- and MO-files for your project as described above.
|
||||
|
||||
4. To merge old PO-file with strings from created new POT-file use command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
msgmerge -N -o new.po old.po new.pot
|
||||
```
|
||||
msgmerge -N -o new.po old.po new.pot
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use option `-N` to not using fuzzy matching when an exact match is not found.
|
||||
|
||||
5. To concatenate old PO-file with strings from new PO-file use command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
msgcat -o new.po old.po
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
msgcat -o new.po old.po
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Create an English translation catalog with command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
msgen -o new.po old.po
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
msgen -o new.po old.po
|
||||
```
|
||||
Notice, in this Catalog it will be totally same strings for initial text and translated.
|
||||
|
||||
When you have Catalog to translation open POT or PO file in PoEdit and start translating.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## General guidelines for Orca Slicer translators
|
||||
|
||||
- We recommend using _PoEdit_ application for translation (as described above). It will help you eliminate most punctuation errors and will show you strings with "random" translations (if the fuzzy parameter was used).
|
||||
|
||||
- We recommend using *PoEdit* application for translation (as described above). It will help you eliminate most punctuation errors and will show you strings with "random" translations (if the fuzzy parameter was used).
|
||||
|
||||
- To check how the translated text looks on the UI elements, test it :) If you use *PoEdit*, all you need to do is save the file. At this point, a MO file will be created. Rename it Orca Slicer.mo, and you can run Orca Slicer (see above).
|
||||
- To check how the translated text looks on the UI elements, test it :) If you use _PoEdit_, all you need to do is save the file. At this point, a MO file will be created. Rename it Orca Slicer.mo, and you can run Orca Slicer (see above).
|
||||
|
||||
- If you see an encoding error (garbage characters instead of Unicode) somewhere in Orca Slicer, report it. It is likely not a problem of your translation, but a bug in the software.
|
||||
|
||||
- See on which UI elements the translated phrase will be used. Especially if it's a button, it is very important to decide on the translation and not write alternative translations in parentheses, as this will significantly increase the width of the button, which is sometimes highly undesirable:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- If you decide to use autocorrect or any batch processing tool, the output requires very careful proofreading. It is very easy to make it do changes that break things big time.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Any formatting parts of the phrases must remain unchanged.** For example, you should not change `%1%` to `%1 %`, you should not change `%%` to `%` (for percent sign) and similar. This will lead to application crashes.
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,4 +106,3 @@ When you have Catalog to translation open POT or PO file in PoEdit and start tra
|
|||
- If the phrase doesn't have a dot at the end, don't add it. And if it does, then don't forget to :)
|
||||
|
||||
- It is useful to stick to the same terminology in the application (especially with basic terms such as "filament" and similar). Stay consistent. Otherwise it will confuse users.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,13 +1,25 @@
|
|||
# Precise Wall
|
||||
|
||||
The 'Precise Wall' is a distinctive feature introduced by OrcaSlicer, aimed at improving the dimensional accuracy of prints and minimizing layer inconsistencies by slightly increasing the spacing between the outer wall and the inner wall.
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a technical explanation of how this feature works.
|
||||
First, it's important to understand some basic concepts like flow, extrusion width, and space. Slic3r has an excellent document that covers these topics in detail. You can refer to this article: [link to article](https://manual.slic3r.org/advanced/flow-math).
|
||||
## Technical explanation
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a technical explanation of how this feature works.
|
||||
|
||||
First, it's important to understand some basic concepts like flow, extrusion width, and space. Slic3r has an excellent document that covers these topics in detail. You can refer to this [article](https://manual.slic3r.org/advanced/flow-math).
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's dive into the specifics. Slic3r and its forks, such as PrusaSlicer, SuperSlicer, and OrcaSlicer, assume that the extrusion path has an oval shape, which accounts for the overlaps. For example, if we set the wall width to 0.4mm and the layer height to 0.2mm, the combined thickness of two walls laid side by side is 0.714mm instead of 0.8mm due to the overlapping.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Precise Wall Off**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Precise Wall On**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's dive into the specifics. Slic3r and its forks, such as PrusaSlicer, SuperSlicer, and OrcaSlicer, assume that the extrusion path has an oval shape, which accounts for the overlaps. For example, if we set the wall width to 0.4mm and the layer height to 0.2mm, the combined thickness of two walls laid side by side is 0.714mm instead of 0.8mm due to the overlapping.
|
||||

|
||||
This approach enhances the strength of 3D-printed parts. However, it does have some side effects. For instance, when the inner-outer wall order is used, the outer wall can be pushed outside, leading to potential size inaccuracy and more layer inconsistency.
|
||||
|
||||
It's important to keep in mind that this approach to handling flow is specific to Slic3r and it's forks. Other slicing software, such as Cura, assumes that the extrusion path is rectangular and, therefore, does not include overlapping. Two 0.4 mm walls will result in a 0.8 mm shell thickness in Cura
|
||||
It's important to keep in mind that this approach to handling flow is specific to Slic3r and its forks. Other slicing software, such as Cura, assumes that the extrusion path is rectangular and, therefore, does not include overlapping. Two 0.4 mm walls will result in a 0.8 mm shell thickness in Cura.
|
||||
|
||||
OrcaSlicer adheres to Slic3r's approach to handling flow. To address the downsides mentioned earlier, OrcaSlicer introduced the 'Precise Wall' feature. When this feature is enabled in OrcaSlicer, the overlap between the outer wall and its adjacent inner wall is set to zero. This ensures that the overall strength of the printed part is unaffected, while the size accuracy and layer consistency are improved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Print settings:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Seam](seam)
|
||||
* [Axiliary fan](auxiliary-fan)
|
||||
* [Chamber temperature](chamber-temperature)
|
||||
* [Air filtration/Exhaust fan](air-filtration)
|
||||
* [Single Extruder Multimaterial](semm)
|
||||
* [Precise wall](Precise-wall)
|
||||
20
doc/Seam.md
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
WIP...
|
||||
|
||||
### Scarf joint seam
|
||||
WIP...
|
||||
|
||||
### Seam gap
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Role-based wipe speed(auto)
|
||||
### Wipe speed
|
||||
### Wipe on loop(inward movement)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use outer wall speed and acceleration instead of travel speed and acceleration.
|
||||
Added an option to disable this feature
|
||||
### Support Cura style outer wall wipe(100% retract before wipe)
|
||||
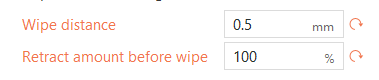
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Extra length on restart
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,44 +1,57 @@
|
|||
# Adaptive Bed Mesh Support
|
||||
Orca Slicer introduces comprehensive support for adaptive bed meshing across a variety of firmware, including Marlin, Klipper, and RepRapFirmware (RRF).
|
||||
This feature allows users to seamlessly integrate adaptive bed mesh commands within the Machine Start G-code.
|
||||
|
||||
Orca Slicer introduces comprehensive support for adaptive bed meshing across a variety of firmware, including Marlin, Klipper, and RepRapFirmware (RRF).
|
||||
|
||||
This feature allows users to seamlessly integrate adaptive bed mesh commands within the Machine Start G-code.
|
||||
|
||||
The implementation is designed to be straightforward, requiring no additional plugins or alterations to firmware settings, thereby enhancing user experience and print quality directly from Orca Slicer.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Settings in Orca Slicer:
|
||||
|
||||
`Bed mesh min`: This option sets the min point for the allowed bed mesh area. Due to the probe's XY offset, most printers are unable to probe the entire bed. To ensure the probe point does not go outside the bed area, the minimum and maximum points of the bed mesh should be set appropriately. OrcaSlicer ensures that adaptive_bed_mesh_min/adaptive_bed_mesh_max values do not exceed these min/max points. This information can usually be obtained from your printer manufacturer. The default setting is (-99999, -99999), which means there are no limits, thus allowing probing across the entire bed.
|
||||
|
||||
`Bed mesh max`: This option sets the max point for the allowed bed mesh area. Due to the probe's XY offset, most printers are unable to probe the entire bed. To ensure the probe point does not go outside the bed area, the minimum and maximum points of the bed mesh should be set appropriately. OrcaSlicer ensures that adaptive_bed_mesh_min/adaptive_bed_mesh_max values do not exceed these min/max points. This information can usually be obtained from your printer manufacturer. The default setting is (99999, 99999), which means there are no limits, thus allowing probing across the entire bed.
|
||||
|
||||
`Probe point distance`: This option sets the preferred distance between probe points (grid size) for the X and Y directions, with the default being 50mm for both X and Y.
|
||||
|
||||
`Mesh margin`: This option determines the additional distance by which the adaptive bed mesh area should be expanded in the XY directions. Note for Klipper users: Orca Slicer will adjust adaptive bed mesh area according to the margin. It is recommended to set the margin to 0 in Klipper config or pass 0 when calling BED_MESH_CALIBRATE command(please refer to the example below).
|
||||
`Mesh margin`: This option determines the additional distance by which the adaptive bed mesh area should be expanded in the XY directions.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Klipper users: Orca Slicer will adjust adaptive bed mesh area according to the margin. It is recommended to set the margin to 0 in Klipper config or pass 0 when calling BED_MESH_CALIBRATE command(please refer to the example below).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available g-code variables for Adaptive Bed Mesh Command
|
||||
|
||||
## Available g-code variables for Adaptive Bed Mesh Command
|
||||
`bed_mesh_probe_count`: Represents the probe count in the X and Y directions. This value is calculated based on the size of the adaptive bed mesh area and the distance between probe points.
|
||||
|
||||
`adaptive_bed_mesh_min`: Specifies the minimum coordinates of the adaptive bed mesh area, defining the starting point of the mesh.
|
||||
|
||||
`adaptive_bed_mesh_max`: Determines the maximum coordinates of the adaptive bed mesh area, indicating the endpoint of the mesh.
|
||||
|
||||
`ALGORITHM`: Identifies the algorithm used for adaptive bed mesh interpolation. This variable is useful for Klipper users. If bed_mesh_probe_count is less than 4, the algorithm is set to `lagrange`. Otherwise, it is set to `bicubic`.
|
||||
`ALGORITHM`: Identifies the algorithm used for adaptive bed mesh interpolation. This variable is useful for Klipper users. If bed_mesh_probe_count is less than 4, the algorithm is set to `lagrange`. Otherwise, it is set to `bicubic`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example of Adaptive Bed Mesh usage in Orca Slicer:
|
||||
## Example of Adaptive Bed Mesh usage in Orca Slicer:
|
||||
|
||||
### Marlin:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
; Marlin don't support speicify the probe count yet, so we only specify the probe area
|
||||
G29 L{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[0]} R{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[0]} F{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[1]} B{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[1]} T V4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Klipper:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
; Always pass `ADAPTIVE_MARGIN=0` because Orca has already handled `adaptive_bed_mesh_margin` internally
|
||||
; Make sure to set ADAPTIVE to 0 otherwise Klipper will use it's own adaptive bed mesh logic
|
||||
BED_MESH_CALIBRATE mesh_min={adaptive_bed_mesh_min[0]},{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[1]} mesh_max={adaptive_bed_mesh_max[0]},{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[1]} ALGORITHM=[bed_mesh_algo] PROBE_COUNT={bed_mesh_probe_count[0]},{bed_mesh_probe_count[1]} ADAPTIVE=0 ADAPTIVE_MARGIN=0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### RRF:
|
||||
|
||||
```gcode
|
||||
M557 X{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[0]}:{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[0]} Y{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[1]}:{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[1]} P{bed_mesh_probe_count[0]}:{bed_mesh_probe_count[1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
M557 X{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[0]}:{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[0]} Y{adaptive_bed_mesh_min[1]}:{adaptive_bed_mesh_max[1]} P{bed_mesh_probe_count[0]}:{bed_mesh_probe_count[1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,10 +1,15 @@
|
|||
# Air Filtration/Exhaust Fan Control in OrcaSlicer
|
||||
|
||||
OrcaSlicer use `M106 P3` command to control air-filtration/exhaust fan.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Klipper, you can define a `M106` macro to control the both normal part cooling fan and auxiliary fan and exhaust fan.
|
||||
Below is a reference configuration for Klipper.
|
||||
*Note: Don't forget to change the pin name to the actual pin name you are using in the configuration*
|
||||
If you are using Klipper, you can define a `M106` macro to control both the normal part cooling fan, auxiliary fan, and exhaust fan.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Below is a reference configuration for Klipper.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Don't forget to change the pin name to the actual pin name you are using in the configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
# instead of using [fan], we define the default part cooling fan with [fan_generic] here
|
||||
# this is the default part cooling fan
|
||||
[fan_generic fan0]
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,5 +36,4 @@ gcode:
|
|||
{% set fan = 'fan' + (params.P|int if params.P is defined else 0)|string %}
|
||||
{% set speed = (params.S|float / 255 if params.S is defined else 1.0) %}
|
||||
SET_FAN_SPEED FAN={fan} SPEED={speed}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -2,15 +2,15 @@
|
|||
|
||||
You can enable it in printer settings.
|
||||
|
||||
Once enabled, you can select the bed type in the drop-down menu, corresponding bed temperature will be set automatically.
|
||||
You can set the bed temperature for each bed type in the filament settings as demonstrated in the following image.
|
||||
|
||||
Once enabled, you can select the bed type in the drop-down menu, corresponding bed temperature will be set automatically.
|
||||
You can set the bed temperature for each bed type in the filament settings as demonstrated in the following image.
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Orca also support `curr_bed_type` variable in custom G-code.
|
||||
For example, the following sample G-codes can detect the selected bed type and adjust the G-code offset accordingly for Klipper:
|
||||
|
||||
Orca also support `curr_bed_type` variable in custom G-code.
|
||||
For example, the following sample G-codes can detect the selected bed type and adjust the G-code offset accordingly for Klipper:
|
||||
```
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
{if curr_bed_type=="Textured PEI Plate"}
|
||||
SET_GCODE_OFFSET Z=-0.05
|
||||
{else}
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,9 +19,10 @@ For example, the following sample G-codes can detect the selected bed type and a
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
available bed types are:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
"Cool Plate"
|
||||
"Engineering Plate"
|
||||
"High Temp Plate"
|
||||
"Textured PEI Plate"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
7
doc/developer-reference/Developers-Home.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|||
# For Developers
|
||||
|
||||
This is a documentation from someone exploring the code and is by no means complete or even completely accurate. Please edit the parts you might find inaccurate. This is probably going to be helpful nonetheless.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Preset, PresetBundle and PresetCollection](Preset-and-bundle)
|
||||
- [Plater, Sidebar, Tab, ComboBox](plater-sidebar-tab-combobox)
|
||||
- [Slicing Call Hierarchy](slicing-hierarchy)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# For Developers
|
||||
|
||||
This is a documentation from someone exploring the code and is by no means complete or even completely accurate. Please edit the parts you might find inaccurate. This is probably going to be helpful nonetheless.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Preset, PresetBundle and PresetCollection](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/doc/developer-reference/Preset-and-bundle.md)
|
||||
- [Plater, Sidebar, Tab, ComboBox](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/doc/developer-reference/plater-sidebar-tab-combobox.md)
|
||||
- [Slicing Call Hierarchy](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/doc/developer-reference/slicing-hierarchy.md)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,26 +1,27 @@
|
|||
This page deals with the explanation for 3 classes in the code.
|
||||
|
||||
## [`Preset`](../../src/libslic3r/Preset.hpp)
|
||||
## [`Preset`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/libslic3r/Preset.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
As the name might suggest this class deals with presets for various things. It defines an enum `Type` which basically tells you what kind of data the present contains. Below are a few explained and there corresponding UI elements
|
||||
|
||||
#### Note: There is a lot of outdated and legacy code in the code base.
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> There is a lot of outdated and legacy code in the code base.
|
||||
|
||||
- `TYPE_PRINT`: Refers to a process preset. It's called 'Print' probably due to some legacy code.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/process-preset.png" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- `TYPE_FILAMENT`: As the name suggests this preset is for filaments
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/filament-preset.png" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- `TYPE_PRINTER`: Preset for printers.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/printer-preset.png" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There are other preset types but some of them are for SLA. Which is legacy code, since SLA printers are no longer supported. Above 3 are the important types.
|
||||
|
||||
## [`PresetBundle`](../../src/libslic3r/PresetBundle.hpp)
|
||||
## [`PresetBundle`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/libslic3r/PresetBundle.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
This is a bundle containing a few types of `PresetCollection`. One bundle has presets for some printers, filaments and some processes (TYPE_PRINT).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,9 +31,10 @@ This is a bundle containing a few types of `PresetCollection`. One bundle has pr
|
|||
|
||||
each one of these contains a collection of processes, filaments and printers respectively.\
|
||||
|
||||
#### Note: Printers, filaments and processes in the bundle don't all have to be compatible with each other. In fact all the saved presets are stored in one `PresetBundle`. The `PresetBundle` is loaded on start up. The list of filaments and processes shown for a particular printer is a subset of `filaments` and `prints` `PresetCollection`s.
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Printers, filaments and processes in the bundle don't all have to be compatible with each other. In fact all the saved presets are stored in one `PresetBundle`. The `PresetBundle` is loaded on start up. The list of filaments and processes shown for a particular printer is a subset of `filaments` and `prints` `PresetCollection`s.
|
||||
|
||||
## [`PresetCollection`](../../src/libslic3r/Preset.hpp)
|
||||
## [`PresetCollection`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/libslic3r/Preset.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
`PrinterPresetCollection` is a class derived from `PresetCollection`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,23 +1,25 @@
|
|||
# Application Structure Overview
|
||||
|
||||
### !! incomplete, possibly inaccurate, being updated with new info !!
|
||||
|
||||
## [`Plater`](../../src/slic3r/GUI/Plater.hpp)
|
||||
## [`Plater`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/slic3r/GUI/Plater.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
Refers to the entire application. The whole view, file loading, project saving and loading is all managed by this class. This class contains members for the model viewer, the sidebar, gcode viewer and everything else.
|
||||
|
||||
## [`Sidebar`](../../src/slic3r/GUI/Plater.hpp)
|
||||
## [`Sidebar`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/slic3r/GUI/Plater.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
This is relating the the sidebar in the application window
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/full-sidebar.png" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## [`ComboBox`](../../src/slic3r/GUI/Widgets/ComboBox.hpp)
|
||||
## [`ComboBox`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/slic3r/GUI/Widgets/ComboBox.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
The drop down menus where you can see and select presets
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/combobox.png" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## [`Tab`](../../src/slic3r/GUI/Tab.hpp)
|
||||
## [`Tab`](https://github.com/SoftFever/OrcaSlicer/blob/main/src/slic3r/GUI/Tab.hpp)
|
||||
|
||||
Refers to the various windows with settings. e.g. the Popup to edit printer or filament preset. Also the section to edit process preset and the object list. These 4 are managed by `TabPrinter`, `TabFilament`, `TabPrint` and `TabPrintModel` respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/tab-popup.png" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||

|
||||
|
|
@ -2,4 +2,43 @@
|
|||
|
||||
The Slicing logic is not the easiest to locate in the code base. Below is a flow diagram of function calls that are made after clicking the `Slice Plate` button in the UI. Most of the processing happens in different threads. Note the calls after `BackgroundSlicingProcess::start()`, but this is how you can find the slicing logic.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="../images/slicing_call_heirarchy.svg" alt="Example Image" width="320">
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
flowchart TD
|
||||
A["Slice plate"] --> B["void Plater::priv::on_action_slice_plate(SimpleEvent&)"]
|
||||
B --> C["void Plater::reslice()"]
|
||||
C --> D["bool Plater::priv::restart_background_process(unsigned int state)"]
|
||||
D --> E["bool BackgroundSlicingProcess::start()"]
|
||||
E --> F["void BackgroundSlicingProcess::thread_proc_safe_seh_throw()"]
|
||||
F --> G["unsigned long BackgroundSlicingProcess::thread_proc_safe_seh()"]
|
||||
G --> H["void BackgroundSlicingProcess::thread_proc_safe()"]
|
||||
H --> I["void BackgroundSlicingProcess::thread_proc()"]
|
||||
I --> J["void BackgroundSlicingProcess::call_process_seh_throw(std::exception_ptr &ex)"]
|
||||
J --> K["unsigned long BackgroundSlicingProcess::call_process_seh(std::exception_ptr &ex)"]
|
||||
K --> L["void BackgroundSlicingProcess::call_process(std::exception_ptr &ex)"]
|
||||
L --> M["void BackgroundSlicingProcess::process_fff()"]
|
||||
M --> N["void Print::process(long long *time_cost_with_cache, bool use_cache)"]
|
||||
N --> O["void PrintObject::make_perimeters()"]
|
||||
O --> P["void PrintObject::slice()"]
|
||||
|
||||
%% Labels for libraries
|
||||
subgraph G1 [libSlic3r_gui]
|
||||
B
|
||||
C
|
||||
D
|
||||
E
|
||||
F
|
||||
G
|
||||
H
|
||||
I
|
||||
J
|
||||
K
|
||||
L
|
||||
M
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
subgraph G2 [libSlic3r]
|
||||
N
|
||||
O
|
||||
P
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
91
doc/fill-patterns.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
|||
# Infill Patterns
|
||||
WIP...
|
||||
|
||||
## Concentric
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Rectilinear
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Grid
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 2D Lattice
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Line
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Cubic
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Triangles
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Tri-hexagon
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Gyroid
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Honeycomb
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Adaptive Cubic
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Aligned Rectilinear
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 3D Honeycomb
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Hilbert Curve
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Archimedean Chords
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Octagram Spiral
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Support Cubic
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Lightning
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Cross Hatch
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Quartered Cubic
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Standard images are taken with:
|
||||
> - Primitive Cube: 66mm x 66mm x 66mm
|
||||
> - Layer Height: 0.2mm
|
||||
> - Infill Density: 15%
|
||||
> - Layer Count: 329
|
||||
> - Wall loops: 3 (Hide in isometric view)
|
||||
> - Anchor: Off
|
||||
BIN
doc/images/Adaptative-Bed-Mesh/ABM-Machine-G-code.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 58 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Adaptative-Bed-Mesh/ABM-PrinterConfig.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Chamber/Chamber-Temperature-Control-Material.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Chamber/Chamber-Temperature-Control-Printer.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 24 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 36 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 24 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 773 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 773 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 783 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 783 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 68 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 68 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 4.4 MiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.4 MiB |
BIN
doc/images/Flow-Rate/flowcalibration_update_flowrate.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Flow-Rate/flowrate-0-5.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 382 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Flow-Rate/flowrate-6.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 738 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Flow-Rate/flowrate-Bambulab-uncheck.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Flow-Rate/flowrate-pass1.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.8 MiB |
BIN
doc/images/Flow-Rate/flowrate-pass2.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 550 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 7.3 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 8.7 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 13 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.9 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.9 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
3
doc/images/PreciseWall/PreciseWallOff.svg
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
|
||||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" style="background: transparent; background-color: transparent; color-scheme: light dark;" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" version="1.1" width="401px" height="71px" viewBox="-0.5 -0.5 401 71"><defs/><g><g data-cell-id="0"><g data-cell-id="1"><g data-cell-id="fhMGX1kBES0GxHB0cy2X-14"><g><rect x="130" y="0" width="140" height="70" rx="25.9" ry="25.9" fill-opacity="0.75" fill="#e3c800" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(227, 200, 0), rgb(103, 80, 0)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(176, 149, 0), rgb(141, 118, 0));" stroke="#b09500" stroke-opacity="0.75" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe center; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 138px; height: 1px; padding-top: 35px; margin-left: 131px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 12px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ededed); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: normal; word-wrap: normal; ">Inner wall</div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="200" y="39" fill="#000000" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="12px" text-anchor="middle">Inner wall</text></switch></g></g></g><g data-cell-id="fhMGX1kBES0GxHB0cy2X-15"><g><rect x="260" y="0" width="140" height="70" rx="25.9" ry="25.9" fill-opacity="0.75" fill="#e3c800" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(227, 200, 0), rgb(103, 80, 0)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(176, 149, 0), rgb(141, 118, 0));" stroke="#b09500" stroke-opacity="0.75" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe center; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 138px; height: 1px; padding-top: 35px; margin-left: 261px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 12px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ededed); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: normal; word-wrap: normal; ">Inner wall</div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="330" y="39" fill="#000000" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="12px" text-anchor="middle">Inner wall</text></switch></g></g></g><g data-cell-id="fhMGX1kBES0GxHB0cy2X-9"><g><rect x="0" y="0" width="140" height="70" rx="25.9" ry="25.9" fill-opacity="0.75" fill="#fa6800" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(250, 104, 0), rgb(233, 107, 18)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(199, 53, 0), rgb(255, 145, 100));" stroke="#c73500" stroke-opacity="0.75" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe center; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 138px; height: 1px; padding-top: 35px; margin-left: 1px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 12px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ededed); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: normal; word-wrap: normal; ">Outer wall</div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="70" y="39" fill="#000000" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="12px" text-anchor="middle">Outer wall</text></switch></g></g></g></g></g></g></svg>
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 4 KiB |
3
doc/images/PreciseWall/PreciseWallOn.svg
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
|
||||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" style="background: transparent; background-color: transparent; color-scheme: light dark;" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" version="1.1" width="411px" height="71px" viewBox="-0.5 -0.5 411 71"><defs/><g><g data-cell-id="0"><g data-cell-id="1"><g data-cell-id="fhMGX1kBES0GxHB0cy2X-14"><g><rect x="140" y="0" width="140" height="70" rx="25.9" ry="25.9" fill-opacity="0.75" fill="#e3c800" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(227, 200, 0), rgb(103, 80, 0)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(176, 149, 0), rgb(141, 118, 0));" stroke="#b09500" stroke-opacity="0.75" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe center; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 138px; height: 1px; padding-top: 35px; margin-left: 141px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 12px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ededed); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: normal; word-wrap: normal; ">Inner wall</div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="210" y="39" fill="#000000" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="12px" text-anchor="middle">Inner wall</text></switch></g></g></g><g data-cell-id="fhMGX1kBES0GxHB0cy2X-15"><g><rect x="270" y="0" width="140" height="70" rx="25.9" ry="25.9" fill-opacity="0.75" fill="#e3c800" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(227, 200, 0), rgb(103, 80, 0)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(176, 149, 0), rgb(141, 118, 0));" stroke="#b09500" stroke-opacity="0.75" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe center; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 138px; height: 1px; padding-top: 35px; margin-left: 271px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 12px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ededed); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: normal; word-wrap: normal; ">Inner wall</div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="340" y="39" fill="#000000" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="12px" text-anchor="middle">Inner wall</text></switch></g></g></g><g data-cell-id="fhMGX1kBES0GxHB0cy2X-9"><g><rect x="0" y="0" width="140" height="70" rx="25.9" ry="25.9" fill-opacity="0.75" fill="#fa6800" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(250, 104, 0), rgb(233, 107, 18)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(199, 53, 0), rgb(255, 145, 100));" stroke="#c73500" stroke-opacity="0.75" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe center; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 138px; height: 1px; padding-top: 35px; margin-left: 1px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 12px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ededed); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: normal; word-wrap: normal; ">Outer wall</div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="70" y="39" fill="#000000" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="12px" text-anchor="middle">Outer wall</text></switch></g></g></g></g></g></g></svg>
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 4 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/PreciseZ/PreciseZOff.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 266 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/PreciseZ/PreciseZOn.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 273 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 14 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 14 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 82 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 82 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 161 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 161 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 154 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 154 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Temp-calib/temp-tower.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 238 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 224 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 224 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Temp-calib/temp-tower_test_menu.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 9.3 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Tolerance/FilamentShrinkageCompensation.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 21 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 21 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/Tolerance/QualityPrecision.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
3
doc/images/Tolerance/tolerance_hole.svg
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
|
||||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" style="background: transparent; background-color: transparent; color-scheme: light dark;" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" version="1.1" width="407px" height="317px" viewBox="-0.5 -0.5 407 317"><defs/><g><g data-cell-id="0"><g data-cell-id="1"><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-10"><g><path d="M 141.5 8 L 316.5 8 L 404 158 L 404 158 L 316.5 308 L 141.5 308 L 54 158 L 54 158 Z" fill="#009688" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 150, 136), rgb(36, 165, 153)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" stroke-width="2" stroke-miterlimit="10" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-20"><g><ellipse cx="229" cy="158" rx="150" ry="150" fill="transparent" stroke="#000000" style="stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke-opacity="0.5" stroke-dasharray="3 3" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-21"><g><ellipse cx="141.5" cy="8.5" rx="2.5" ry="2.5" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(237, 237, 237)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-22"><g><ellipse cx="316.5" cy="8.5" rx="2.5" ry="2.5" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(237, 237, 237)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-23"><g><ellipse cx="141.5" cy="307.5" rx="2.5" ry="2.5" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(237, 237, 237)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-24"><g><ellipse cx="316.5" cy="307.5" rx="2.5" ry="2.5" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(237, 237, 237)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-25"><g><ellipse cx="54.5" cy="158" rx="2.5" ry="2.5" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(237, 237, 237)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-26"><g><ellipse cx="403.5" cy="158" rx="2.5" ry="2.5" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(237, 237, 237)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" pointer-events="all"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-27"><g><path d="M 137 8.73 L 4 8" fill="none" stroke="#000000" style="stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke-miterlimit="10" pointer-events="stroke"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-28"><g><path d="M 137 307.86 L 4 307" fill="none" stroke="#000000" style="stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke-miterlimit="10" pointer-events="stroke"/></g></g><g data-cell-id="S3ItyMhgztYiZC9E-VA5-29"><g><path d="M 14 300.63 L 14 14.37" fill="none" stroke="#000000" style="stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke-miterlimit="10" pointer-events="stroke"/><path d="M 14 305.88 L 10.5 298.88 L 14 300.63 L 17.5 298.88 Z" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" stroke-miterlimit="10" pointer-events="all"/><path d="M 14 9.12 L 17.5 16.12 L 14 14.37 L 10.5 16.12 Z" fill="#000000" style="fill: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255)); stroke: light-dark(rgb(0, 0, 0), rgb(255, 255, 255));" stroke="#000000" stroke-miterlimit="10" pointer-events="all"/></g><g><g transform="translate(-0.5 -0.5)rotate(-90 14 154.83333333333326)"><switch><foreignObject style="overflow: visible; text-align: left;" pointer-events="none" width="100%" height="100%" requiredFeatures="http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/feature#Extensibility"><div xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" style="display: flex; align-items: unsafe flex-end; justify-content: unsafe center; width: 1px; height: 1px; padding-top: 155px; margin-left: 14px;"><div style="box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 0; text-align: center; color: #000000; "><div style="display: inline-block; font-size: 11px; font-family: "Helvetica"; color: light-dark(#000000, #ffffff); line-height: 1.2; pointer-events: all; white-space: nowrap; "><font face="Verdana">6,00mm</font></div></div></div></foreignObject><text x="14" y="155" fill="light-dark(#000000, #ffffff)" font-family=""Helvetica"" font-size="11px" text-anchor="middle">6,00mm</text></switch></g></g></g></g></g></g></svg>
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.7 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/calibration.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 3.4 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.6 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 4.4 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.8 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-2d-lattice.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 130 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-3d-honeycomb.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 602 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-adaptative-cubic.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 708 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-aligned-rectilinear.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 426 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-archimedean-chords.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 864 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-concentric.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 537 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-cross-hatch.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 597 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-cubic.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 795 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-grid.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 248 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-gyroid.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 958 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-hilbert-curve.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 322 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-honeycomb.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 504 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-lightning.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 355 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-line.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 788 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-octagram-spiral.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 490 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-quarter-cubic.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 434 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-rectilinear.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 365 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-support-cubic.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 545 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-tri-hexagon.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 584 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-iso-triangles.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 566 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-2d-lacttice.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 154 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-3d-honeycomb.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 266 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-adaptative-cubic.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 496 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-aligned-rectilinear.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 88 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-archimedean-chords.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 340 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-concentric.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 47 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-cross-hatch.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 446 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-cubic.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 591 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-grid.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 83 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-gyroid.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.2 MiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-hilbert-curve.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 99 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-honeycomb.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 316 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-lightning.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 229 KiB |
BIN
doc/images/fill/infill-top-line.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 292 KiB |